HGF converts ErbB2/Neu epithelial morphogenesis to cell invasion
- PMID: 15548598
- PMCID: PMC545891
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-07-0567
HGF converts ErbB2/Neu epithelial morphogenesis to cell invasion
Abstract
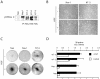
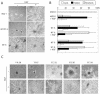
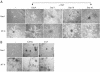
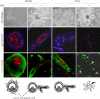
Activation of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor Met induces a morphogenic response and stimulates the formation of branching tubules by Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) epithelial cells in three-dimensional cultures. A constitutively activated ErbB2/Neu receptor, NeuNT, promotes a similar invasive morphogenic program in MDCK cells. Because both receptors are expressed in breast epithelia, are associated with poor prognosis, and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is expressed in stroma, we examined the consequence of cooperation between these signals. We show that HGF disrupts NeuNT-induced epithelial morphogenesis, stimulating the breakdown of cell-cell junctions, dispersal, and invasion of single cells. This correlates with a decrease in junctional proteins claudin-1 and E-cadherin, in addition to the internalization of the tight junction protein ZO-1. HGF-induced invasion of NT-expressing cells is abrogated by pretreatment with a pharmacological inhibitor of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) pathway, which restores E-cadherin and ZO-1 at cell-cell junctions, establishing the involvement of MEK-dependent pathways in this process. These results demonstrate that physiological signals downstream from the HGF/Met receptor synergize with ErbB2/Neu to enhance the malignant phenotype, promoting the breakdown of cell-cell junctions and enhanced cell invasion. This is particularly important for cancers where ErbB2/Neu is overexpressed and HGF is a physiological growth factor found in the stroma.
Figures
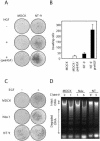


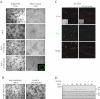
References
-
- Balda, M. S., and Matter, K. (2003). Epithelial cell adhesion and the regulation of gene expression. Trends Cell Biol. 13, 310-318. - PubMed
-
- Birchmeier, W., and Behrens, J. (1994). Cadherin expression in carcinomas: role in the formation of cell junctions and the prevention of invasiveness. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1198, 11-26. - PubMed
-
- Blanco, D., Vicent, S., Elizegi, E., Pino, I., Fraga, M. F., Esteller, M., Saffiotti, U., Lecanda, F., and Montuenga, L. M. (2004). Altered expression of adhesion molecules and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in silica-induced rat lung carcinogenesis. Lab. Investig. 84, 999-1012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

