Identification and characterization of regulator of G protein signaling 4 (RGS4) as a novel inhibitor of tubulogenesis: RGS4 inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinases and vascular endothelial growth factor signaling
- PMID: 15548600
- PMCID: PMC545898
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-06-0479
Identification and characterization of regulator of G protein signaling 4 (RGS4) as a novel inhibitor of tubulogenesis: RGS4 inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinases and vascular endothelial growth factor signaling
Abstract
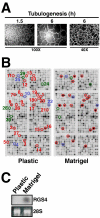
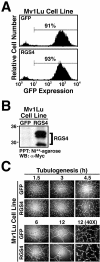
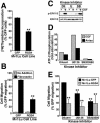
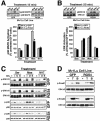
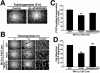
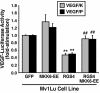
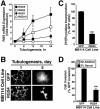
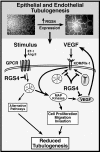
Tubulogenesis by epithelial cells regulates kidney, lung, and mammary development, whereas that by endothelial cells regulates vascular development. Although functionally dissimilar, the processes necessary for tubulation by epithelial and endothelial cells are very similar. We performed microarray analysis to further our understanding of tubulogenesis and observed a robust induction of regulator of G protein signaling 4 (RGS4) mRNA expression solely in tubulating cells, thereby implicating RGS4 as a potential regulator of tubulogenesis. Accordingly, RGS4 overexpression delayed and altered lung epithelial cell tubulation by selectively inhibiting G protein-mediated p38 MAPK activation, and, consequently, by reducing epithelial cell proliferation, migration, and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The tubulogenic defects imparted by RGS4 in epithelial cells, including its reduction in VEGF expression, were rescued by overexpression of constitutively active MKK6, an activator of p38 MAPK. Similarly, RGS4 overexpression abrogated endothelial cell angiogenic sprouting by inhibiting their synthesis of DNA and invasion through synthetic basement membranes. We further show that RGS4 expression antagonized VEGF stimulation of DNA synthesis and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/ERK2 and p38 MAPK activation as well as ERK1/ERK2 activation stimulated by endothelin-1 and angiotensin II. RGS4 had no effect on the phosphorylation of Smad1 and Smad2 by bone morphogenic protein-7 and transforming growth factor-beta, respectively, indicating that RGS4 selectively inhibits G protein and VEGF signaling in endothelial cells. Finally, we found that RGS4 reduced endothelial cell response to VEGF by decreasing VEGF receptor-2 (KDR) expression. We therefore propose RGS4 as a novel antagonist of epithelial and endothelial cell tubulogenesis that selectively antagonizes intracellular signaling by G proteins and VEGF, thereby inhibiting cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and VEGF and KDR expression.
Figures


References
-
- Acarregui, M. J., Penisten, S. T., Goss, K. L., Ramirez, K., and Snyder, J. M. (1999). Vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression in human fetal lung in vitro. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 20, 14-23. - PubMed
-
- Akeson, A. L., Greenberg, J. M., Cameron, J. E., Thompson, F. Y., Brooks, S. K., Wiginton, D., and Whitsett, J. A. (2003). Temporal and spatial regulation of VEGF-A controls vascular patterning in the embryonic lung. Dev. Biol. 264, 443-455. - PubMed
-
- Bagnato, A., and Spinella, F. (2002). Emerging role of endothelin-1 in tumor angiogenesis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 14, 44-50. - PubMed
-
- Bell, S. E., Mavila, A., Salazar, R., Bayless, K. J., Kanagala, S., Maxwell, S. A., and Davis, G. E. (2001). Differential gene expression during capillary morphogenesis in 3D collagen matrices: regulated expression of genes involved in basement membrane matrix assembly, cell cycle progression, cellular differentiation and G-protein signaling. J. Cell Sci. 114, 2755-2773. - PubMed
-
- Berman, D. M., and Gilman, A. G. (1998). Mammalian RGS proteins: barbarians at the gate. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 1269-1272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

