The structure of carbonmonoxy neuroglobin reveals a heme-sliding mechanism for control of ligand affinity
- PMID: 15548613
- PMCID: PMC536024
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0407633101
The structure of carbonmonoxy neuroglobin reveals a heme-sliding mechanism for control of ligand affinity
Abstract
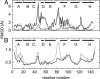
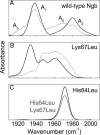
Neuroglobin (Ngb), a globular heme protein expressed in the brain of vertebrates, binds oxygen reversibly, with an affinity comparable to myoglobin (Mb). Despite low sequence identity, the overall 3D fold of Ngb and Mb is very similar. Unlike in Mb, in Ngb the sixth coordination position of the heme iron is occupied by the distal histidine, in the absence of an exogenous ligand. Endogenous ligation has been proposed as a unique mechanism for affinity regulation and ligand discrimination in heme proteins. This peculiarity might be related to the still-unknown physiological function of Ngb. Here, we present the x-ray structure of CO-bound ferrous murine Ngb at 1.7 A and a comparison with the 1.5-A structure of ferric bis-histidine Ngb. We have also used Fourier transform IR spectroscopy of WT and mutant CO-ligated Ngb to examine structural heterogeneity in the active site. Upon CO binding, the distal histidine retains (by and large) its position, whereas the heme group slides deeper into a preformed crevice, thereby reshaping the large cavity ( approximately 290 A(3)) connecting the distal and proximal heme sides with the bulk. The heme relocation is accompanied by a significant decrease of structural disorder, especially of the EF loop, which may be the signal whereby Ngb communicates hypoxic conditions. This unexpected structural change unveils a heme-sliding mechanism of affinity control that may be of significance to understanding Ngb's role in the pathophysiology of the brain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular dynamics simulation of deoxy and carboxy murine neuroglobin in water.Biophys J. 2007 Jul 15;93(2):434-41. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.099648. Epub 2007 Apr 27. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17468165 Free PMC article.
-
Structural characterization of the proximal and distal histidine environment of cytoglobin and neuroglobin.Biochemistry. 2005 Oct 11;44(40):13257-65. doi: 10.1021/bi050997o. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 16201751
-
Heme orientation modulates histidine dissociation and ligand binding kinetics in the hexacoordinated human neuroglobin.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2013 Jan;18(1):111-22. doi: 10.1007/s00775-012-0956-2. Epub 2012 Nov 8. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2013. PMID: 23135388 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible hexa- to penta-coordination of the heme Fe atom modulates ligand binding properties of neuroglobin and cytoglobin.IUBMB Life. 2004 Nov-Dec;56(11-12):657-64. doi: 10.1080/15216540500078830. IUBMB Life. 2004. PMID: 15804829 Review.
-
Neuroglobin, seven years after.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 May;64(10):1259-68. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7090-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17385072 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroglobin, a Factor Playing for Nerve Cell Survival.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Oct 31;17(11):1817. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111817. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27809238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ligand migration through the internal hydrophobic cavities in human neuroglobin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Nov 10;106(45):18984-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905433106. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19850865 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand migration and binding in the dimeric hemoglobin of Scapharca inaequivalvis.Biochemistry. 2007 Dec 11;46(49):14018-31. doi: 10.1021/bi7016798. Epub 2007 Nov 15. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 18001141 Free PMC article.
-
Open and Lys-His Hexacoordinated Closed Structures of a Globin with Swapped Proximal and Distal Sites.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 22;5:11407. doi: 10.1038/srep11407. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26094577 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand pathways in neuroglobin revealed by low-temperature photodissociation and docking experiments.IUCrJ. 2019 Jul 10;6(Pt 5):832-842. doi: 10.1107/S2052252519008157. eCollection 2019 Sep 1. IUCrJ. 2019. PMID: 31576217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burmester, T., Weich, B., Reinhardt, S. & Hankeln, T. (2000) Nature 407, 520–523. - PubMed
-
- Pesce, A., Dewilde, S., Nardini, M., Moens, L., Ascenzi, P., Hankeln, T., Burmester, T. & Bolognesi, M. (2003) Structure (London) 11, 1087–1095. - PubMed
-
- Vallone, B., Nienhaus, K., Brunori, M. & Nienhaus, G. U. (2004) Proteins 56, 85–92. - PubMed
-
- Bashford, D., Chothia, C. & Lesk, A. M. (1987) J. Mol. Biol. 196, 199–216. - PubMed
-
- Dewilde, S., Kiger, L., Burmester, T., Hankeln, T., Baudin-Creuza, V., Aerts, T., Marden, M. C., Caubergs, R. & Moens, L. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 38949–38955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

