Stimulus and potassium-induced epileptiform activity in the human dentate gyrus from patients with and without hippocampal sclerosis
- PMID: 15548657
- PMCID: PMC6730304
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2074-04.2004
Stimulus and potassium-induced epileptiform activity in the human dentate gyrus from patients with and without hippocampal sclerosis
Abstract
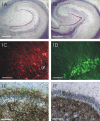
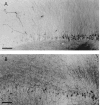
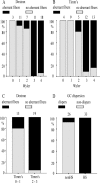
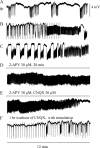
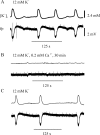
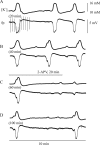
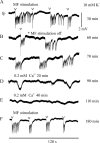
Hippocampal specimens resected to cure medically intractable temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) provide a unique possibility to study functional consequences of morphological alterations. One intriguing alteration predominantly observed in cases of hippocampal sclerosis is an uncommon network of granule cells monosynaptically interconnected via aberrant supragranular mossy fibers. We investigated whether granule cell populations in slices from sclerotic and nonsclerotic hippocampi would develop ictaform activity when challenged by low-frequency hilar stimulation in the presence of elevated extracellular potassium concentration (10 and 12 mm) and whether the experimental activity differs according to the presence of aberrant mossy fibers. We found that ictaform activity could be evoked in slices from sclerotic and nonsclerotic hippocampi (27 of 40 slices, 14 of 20 patients; and 11 of 22 slices, 6 of 12 patients, respectively). However, the two patient groups differed with respect to the pattern of ictaform discharges and the potassium concentration mandatory for its induction. Seizure-like events were already induced with 10 mm K+. They exclusively occurred in slices from sclerotic hippocampi, of which 80% displayed stimulus-induced oscillatory population responses (250-300 Hz). In slices from nonsclerotic hippocampi, atypical negative field potential shifts were predominantly evoked with 12 mm K+. In both groups, the ictaform activity was sensitive to ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists and lowering of [Ca2+]o. Our results show that, in granule cell populations of hippocampal slices from TLE patients, high K+-induced seizure-like activity and ictal spiking coincide with basic electrophysiological abnormalities, hippocampal sclerosis, and mossy fiber sprouting, suggesting that network reorganization could play a crucial role in determining type and threshold of such activity.
Figures



References
-
- Babb TL, Brown WJ, Pretorius JK, Davenport CJ, Lieb JP, Crandall PH (1984) Temporal lobe volumetric cell densities in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 25: 729-740. - PubMed
-
- Babb TL, Kupfer WR, Pretorius JK, Crandall PH, Lévesque MF (1991) Synaptic reorganization by mossy fibers in human epileptic fascia dentata. Neuroscience 42: 351-363. - PubMed
-
- Babb TL, Mathern GW, Leite JP, Pretorius JK, Yeoman KM, Kuhlman PA (1996) Glutamate AMPA receptors in the fascia dentata of human and kainate rat hippocampal epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 26: 193-205. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner C, Elger CE, Hufnagel A, Oppel F, Runge U, Schramm J, Stefan H, Steinhoff BJ, Wieser HG, Zentner J (2000) Qualitätsrichtlinien auf dem Gebiet der prächirurgischen Epilepsiediagnostik und operativen Epilepsietherapie. Akt Neurol 27: 88-89.
-
- Beck H, Blümcke I, Kral T, Clusmann H, Schramm J, Wiestler OD, Heinemann U, Elger CE (1996) Properties of a delayed rectifier potassium current in dentate granule cells isolated from the hippocampus of patients with chronic temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 37: 892-901. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
