Structural basis for the entrance into the phenylpropanoid metabolism catalyzed by phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
- PMID: 15548745
- PMCID: PMC535883
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.104.025288
Structural basis for the entrance into the phenylpropanoid metabolism catalyzed by phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
Abstract
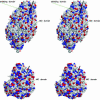
Because of its key role in secondary phenylpropanoid metabolism, Phe ammonia-lyase is one of the most extensively studied plant enzymes. To provide a basis for detailed structure-function studies, the enzyme from parsley (Petroselinum crispum) was crystallized, and the structure was elucidated at 1.7-A resolution. It contains the unusual electrophilic 4-methylidene-imidazole-5-one group, which is derived from a tripeptide segment in two autocatalytic dehydration reactions. The enzyme resembles His ammonia-lyase from the general His degradation pathway but contains 207 additional residues, mainly in an N-terminal extension rigidifying a domain interface and in an inserted alpha-helical domain restricting the access to the active center. Presumably, Phe ammonia-lyase developed from His ammonia-lyase when fungi and plants diverged from the other kingdoms. A pathway of the catalyzed reaction is proposed in agreement with established biochemical data. The inactivation of the enzyme by a nucleophile is described in detail.
Figures







References
-
- Allwood, E.G., Davies, D.R., Gerrish, C., Ellis, B.E., and Bolwell, G.P. (1999). Phosphorylation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase: Evidence for a novel protein kinase and identification of the phosphorylated residue. FEBS Lett. 457, 47–52. - PubMed
-
- Ambrus, C.M., Ambrus, J.L., Horvath, C., Pedersen, H., Sharma, S., Kant, C., Mirand, E., Guthrie, R., and Paul, T. (1978). Phenylalanine depletion for the management of phenylketonuria: Use of enzyme reactors with immobilized enzymes. Science 201, 837–839. - PubMed
-
- Appert, C., Zon, J., and Amrhein, N. (2003). Kinetic analysis of the inhibition of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase by 2-aminoindan-2-phosphonic acid and other phenylalanine analogues. Phytochemistry 62, 415–422. - PubMed
-
- Baedeker, M., and Schulz, G.E. (1999). Overexpression of a designed 2.2 kb gene of eukaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 457, 57–60. - PubMed
-
- Baedeker, M., and Schulz, G.E. (2002. a). Autocatalytic peptide cyclization during chain folding of histidine ammonia-lyase. Structure 10, 61–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

