The relation between c-myc expression and interferon sensitivity in uveal melanoma
- PMID: 15548813
- PMCID: PMC1772437
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2003.033498
The relation between c-myc expression and interferon sensitivity in uveal melanoma
Abstract
Background/aim: Interferons (IFN) are currently being used to treat melanoma, including some patients with uveal melanoma. IFN is thought to inhibit tumour growth through downregulation of the c-myc oncogene; the overexpression of which has been shown to be associated with resistance in cell lines. The aim of this study was to investigate the relation between c-myc gene expression and IFN sensitivity in a series of uveal melanomas in a short term chemosensitivity assay.
Methods: Tumours from 45 patients with uveal melanoma who had undergone enucleation were studied. The ATP chemosensitivity assay was used to study sensitivity to IFN-alpha-2b in freshly isolated cells from each tumour. Flow cytometry was used to assess c-myc expression in formalin fixed material from the primary specimens.
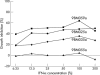
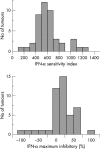
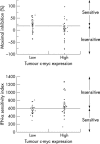
Results: There was a wide range of IFN sensitivity between the specimens whereas c-myc expression was universal and present in 80% of the tumour cells in 80% of the specimens. Higher c-myc expression was associated with IFN-alpha resistance as measured by the maximum percentage of inhibition (p = 0.05) and there was a trend with the IFN sensitivity index (p = 0.07).
Conclusions: These results demonstrate that tumours with high c-myc expression are also associated with IFN resistance. Future research is required to explore the potential of c-myc gene manipulation combined with IFN therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adjuvant interferon therapy for patients with uveal melanoma at high risk of metastasis.Ophthalmology. 2009 Nov;116(11):2206-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.04.044. Epub 2009 Sep 10. Ophthalmology. 2009. PMID: 19744725 Clinical Trial.
-
Decitabine up-regulates S100A2 expression and synergizes with IFN-gamma to kill uveal melanoma cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Sep 1;13(17):5219-25. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0816. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17785578
-
Inverse correlation between expression of HLA-B and c-myc in uveal melanoma.J Pathol. 1997 Jan;181(1):75-9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199701)181:1<75::AID-PATH724>3.0.CO;2-V. J Pathol. 1997. PMID: 9072006
-
[Metastatic uveal melanoma. Development of neoadjuvant treatment in animal experiments].Ophthalmologe. 2001 Aug;98(8):761-5. doi: 10.1007/s003470170084. Ophthalmologe. 2001. PMID: 11552416 Review. German.
-
Selumetinib for the treatment of metastatic uveal melanoma: past and future perspectives.Future Oncol. 2016 Jun;12(11):1331-44. doi: 10.2217/fon-2015-0075. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Future Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27044592 Review.
Cited by
-
Acetaminophen modulates the transcriptional response to recombinant interferon-beta.PLoS One. 2010 Jun 9;5(6):e11031. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011031. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20544007 Free PMC article.
-
N-Myc expression enhances the oncolytic effects of vesicular stomatitis virus in human neuroblastoma cells.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2016 Mar 16;3:16005. doi: 10.1038/mto.2016.5. eCollection 2016. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2016. PMID: 27626059 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of DEAD-box RNA helicase 52 (DDX52) suppresses the proliferation of melanoma cells in vitro and of nude mouse xenografts by targeting c-Myc.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):3539-3549. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1950283. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34233596 Free PMC article.
-
The sodium pump alpha1 sub-unit: a disease progression-related target for metastatic melanoma treatment.J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Sep;13(9B):3960-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00708.x. Epub 2009 Feb 20. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19243476 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Prognostic Fatty Acid Metabolism lncRNAs and Potential Molecular Targeting Drugs in Uveal Melanoma.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Oct 11;2022:3726351. doi: 10.1155/2022/3726351. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9813652. doi: 10.1155/2023/9813652. PMID: 36267302 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Woll E , Bedikian A, Legha SS. Uveal melanoma: natural history and treatment options for metastatic disease. Melanoma Res 1999;9:575–81. - PubMed
-
- Pyrhonen S . The treatment of metastatic uveal melanoma. Eur J Cancer 1998;34 (Suppl 3) :S27–30. - PubMed
-
- Nathan FE, Berd D, Sato T, et al. BOLD+interferon in the treatment of metastatic uveal melanoma: first report of active systemic therapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 1997;16:201–8. - PubMed
-
- Pyrhonen S , Hahka-Kemppinen M, Muhonen T, et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with bleomycin, vincristine, lomustine, dacarbazine (BOLD), and human leukocyte interferon for metastatic uveal melanoma. Cancer 2002;95:2366–72. - PubMed
-
- Cree IA. Cytokine therapy and ocular melanoma. In: Zierhut M, Jager MJ, Ksander BR, eds. Immunology of ocular tumours. Lisse: Swets and Zeitlinger, 2002:147–55.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
