The value of electromyography of the lumbar paraspinal muscles in discriminating between chronic-low-back-pain sufferers and normal subjects
- PMID: 15549487
- PMCID: PMC3476699
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-004-0792-3
The value of electromyography of the lumbar paraspinal muscles in discriminating between chronic-low-back-pain sufferers and normal subjects
Abstract
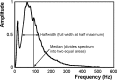
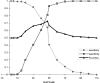
The authors studied the surface electromyographic (EMG) spectrum of the paraspinal muscles of 350 subjects. They were classified by their history as normal (n=175), chronic low back pain (n=145), or past history (n=30). They pulled upwards on a floor-mounted load cell at two-thirds of their maximum voluntary contraction for 30 s, while the EMG was measured from the paraspinal muscles at the L4/L5 level. From the EMG signal the root-mean-square (RMS) was calculated. Power spectrum analysis allowed calculation of the median frequency slope, the initial median frequency (IMF), modal frequency, peak amplitude and spectral width at half peak amplitude (half-width). All of the variables of the chronic group were significantly different from the normal group, except the median frequency slope, RMS slope and mode. Half-width, age and maximum voluntary contraction were shown to be independent predictors of back pain classification. Half-width classified the subjects with a sensitivity of 0.65 and a specificity of 0.75.
Figures

Comment in
-
The Michel Benoist and Robert Mulholland yearly European Spine Journal review: a survey of the "surgical and research" articles in the European Spine Journal, 2005.Eur Spine J. 2006 Jan;15(1):8-15. doi: 10.1007/s00586-005-1062-8. Epub 2006 Jan 13. Eur Spine J. 2006. PMID: 16411129 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Lumbar muscle fatigue and recovery in patients with long-term low-back trouble--electromyography and health-related factors.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2003 Aug;18(7):619-30. doi: 10.1016/s0268-0033(03)00095-0. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2003. PMID: 12880709 Clinical Trial.
-
EMG analysis of lumbar paraspinal muscles as a predictor of the risk of low-back pain.Eur Spine J. 2010 Jul;19(7):1145-52. doi: 10.1007/s00586-010-1277-1. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Eur Spine J. 2010. PMID: 20127260 Free PMC article.
-
Factors in the reproducibility of electromyographic power spectrum analysis of lumbar paraspinal muscle fatigue.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999 May 1;24(9):883-8. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199905010-00009. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999. PMID: 10327510
-
Classification of paraspinal muscle impairments by surface electromyography.Phys Ther. 1998 Aug;78(8):838-51. doi: 10.1093/ptj/78.8.838. Phys Ther. 1998. PMID: 9711209 Review.
-
EMG assessment of back muscle function during cyclical lifting.J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 1998 Aug;8(4):233-45. doi: 10.1016/s1050-6411(98)00010-8. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 1998. PMID: 9779397 Review.
Cited by
-
Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging measurements of the cross-sectional area of the muscle contractile and non-contractile components.Surg Radiol Anat. 2011 Oct;33(8):735-41. doi: 10.1007/s00276-011-0825-7. Epub 2011 May 27. Surg Radiol Anat. 2011. PMID: 21618015
-
Assessment of isokinetic trunk muscle strength and its association with health-related quality of life in patients with degenerative spinal deformity.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 Dec 9;21(1):827. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03844-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 33298028 Free PMC article.
-
Association between spectral characteristics of paraspinal muscles and functional disability in patients with low back pain: a cohort study.BMJ Open. 2018 Feb 14;8(2):e017091. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017091. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 29444776 Free PMC article.
-
The Application of Surface Electromyography Technology in Evaluating Paraspinal Muscle Function.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 May 24;14(11):1086. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14111086. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Michel Benoist and Robert Mulholland yearly European Spine Journal review: a survey of the "surgical and research" articles in the European Spine Journal, 2005.Eur Spine J. 2006 Jan;15(1):8-15. doi: 10.1007/s00586-005-1062-8. Epub 2006 Jan 13. Eur Spine J. 2006. PMID: 16411129 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

