Cysteine and keto acids modulate mosquito kynurenine aminotransferase catalyzed kynurenic acid production
- PMID: 15556614
- PMCID: PMC2855840
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.09.088
Cysteine and keto acids modulate mosquito kynurenine aminotransferase catalyzed kynurenic acid production
Abstract
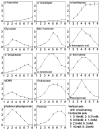
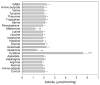
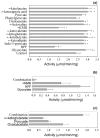
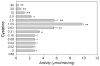
Kynurenine aminotransferase (KAT) catalyzes the formation of kynurenic acid (KYNA), the natural antagonist of ionotropic glutamate receptors. This study tests potential substrates and assesses the effects of amino acids and keto acids on the activity of mosquito KAT. Various keto acids, when simultaneously present in the same reaction mixture, display a combined effect on KAT catalyzed KYNA production. Moreover, methionine and glutamine show inhibitory effects on KAT activity, while cysteine functions as either an antagonist or an inhibitor depending on the concentration. Therefore, the overall level of keto acids and cysteine might modulate the KYNA synthesis. Results from this study will be useful in the study of KAT regulation in other animals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
L-cysteine sulphinate, endogenous sulphur-containing amino acid, inhibits rat brain kynurenic acid production via selective interference with kynurenine aminotransferase II.Neurosci Lett. 2003 Jul 31;346(1-2):97-100. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(03)00579-2. Neurosci Lett. 2003. PMID: 12850557
-
Demonstration of kynurenine aminotransferases I and II and characterization of kynurenic acid synthesis in oligodendrocyte cell line (OLN-93).Neurochem Res. 2005 Aug;30(8):963-8. doi: 10.1007/s11064-005-6178-z. Neurochem Res. 2005. PMID: 16258845
-
Dual effect of DL-homocysteine and S-adenosylhomocysteine on brain synthesis of the glutamate receptor antagonist, kynurenic acid.J Neurosci Res. 2005 Feb 1;79(3):375-82. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20359. J Neurosci Res. 2005. PMID: 15605380
-
The role of glutamine transaminase K (GTK) in sulfur and alpha-keto acid metabolism in the brain, and in the possible bioactivation of neurotoxicants.Neurochem Int. 2004 Jun;44(8):557-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2003.12.002. Neurochem Int. 2004. PMID: 15016471 Review.
-
Kynurenic acid and kynurenine aminotransferases in retinal aging and neurodegeneration.Pharmacol Rep. 2011;63(6):1324-34. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(11)70697-1. Pharmacol Rep. 2011. PMID: 22358081 Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical and structural properties of mouse kynurenine aminotransferase III.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Feb;29(3):784-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01272-08. Epub 2008 Nov 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19029248 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and molecular characterization of tick kynurenine aminotransferase (HlKAT) from Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae).Parasitol Res. 2009 Sep;105(3):669-79. doi: 10.1007/s00436-009-1439-4. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Parasitol Res. 2009. PMID: 19381689
-
Structural insight into the inhibition of human kynurenine aminotransferase I/glutamine transaminase K.J Med Chem. 2009 May 14;52(9):2786-93. doi: 10.1021/jm9000874. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19338303 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, expression, and function of kynurenine aminotransferases in human and rodent brains.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Feb;67(3):353-68. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0166-4. Epub 2009 Oct 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 19826765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural insight into the mechanism of substrate specificity of aedes kynurenine aminotransferase.Biochemistry. 2008 Feb 12;47(6):1622-30. doi: 10.1021/bi701800j. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18186649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moroni F. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999;375:87–100. - PubMed
-
- Schwarcz R, Pellicciari R. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;303:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Stone TW, Darlington LG. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1:609–620. - PubMed
-
- Scharfman HE, Goodman JH, Schwarcz R. Amino Acids. 2000;19:283–297. - PubMed
-
- Erhardt S, Hajos M, Lindberg A, Engberg G. Synapse. 2000;37:104–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

