Dynamical resonance can account for seasonality of influenza epidemics
- PMID: 15557003
- PMCID: PMC534740
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0407293101
Dynamical resonance can account for seasonality of influenza epidemics
Abstract
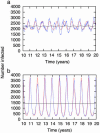
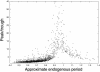
Influenza incidence exhibits strong seasonal fluctuations in temperate regions throughout the world, concentrating the mortality and morbidity burden of the disease into a few months each year. The cause of influenza's seasonality has remained elusive. Here we show that the large oscillations in incidence may be caused by undetectably small seasonal changes in the influenza transmission rate that are amplified by dynamical resonance.
Figures
References
-
- Earn, D. J. D., Dushoff, J. & Levin, S. A. (2002) Trends Ecol. Evol. 17, 334-340.
-
- Huntington, E. (1920) Ecology 1, 6-23.
-
- Schulman, J. L. & Kilbourne, E. D. (1962) Nature 195, 1129-1130. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, R. M. & May, R. M. (1991) Infectious Diseases of Humans: Dynamics and Control (Oxford Science, Oxford).
-
- Nelson, R. J., Demas, G. E., Klein, S. L. & Kriegsfeld, L. J. (2002) Seasonal Patterns of Stress, Immune Function and Disease (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

