Correction of kinetic and stability defects by tetrahydrobiopterin in phenylketonuria patients with certain phenylalanine hydroxylase mutations
- PMID: 15557004
- PMCID: PMC534739
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0407256101
Correction of kinetic and stability defects by tetrahydrobiopterin in phenylketonuria patients with certain phenylalanine hydroxylase mutations
Abstract
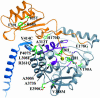
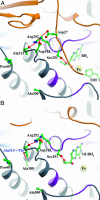
Phenylketonuria patients harboring a subset of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) mutations have recently shown normalization of blood phenylalanine levels upon oral administration of the PAH cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin [(6R)-L-erythro-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)]. Several hypotheses have been put forward to explain BH4 responsiveness, but the molecular basis for the corrective effect(s) of BH4 has not been understood. We have investigated the biochemical, kinetic, and structural changes associated with BH4-responsive mutations (F39L, I65T, R68S, H170D, E178G, V190A, R261Q, A300S, L308F, A313T, A373T, V388M, E390G, P407S, and Y414C). The biochemical and kinetic characterization of the 15 mutants studied points toward a multifactorial basis for the BH4 responsiveness; the mutants show residual activity (>30% of WT) and display various kinetic defects, including increased Km (BH4) and reduced cooperativity of substrate binding, but no decoupling of cofactor (BH4) oxidation. For some, BH4 seems to function through stabilization and protection of the enzyme from inactivation and proteolytic degradation. In the crystal structures of a phenylketonuria mutant, A313T, minor changes were seen when compared with the WT PAH structures, consistent with the mild effects the mutant has upon activity of the enzyme both in vitro and in vivo. Truncations made in the A313T mutant PAH form revealed that the N and C termini of the enzyme influence active site binding. Of fundamental importance is the observation that BH4 appears to increase Phe catabolism if at least one of the two heterozygous mutations has any residual activity remaining.
Figures
References
-
- Scriver, C. R. & Kaufman, S. (2001) in The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, eds. Scriver, C. R., Beaudet, A. L., Sly, W. S. & Valle, D. (McGraw–Hill, New York), pp. 1667-1724.
-
- Scriver, C. R., Hurtubise, M., Konecki, D., Phommarinh, M., Prevost, L., Erlandsen, H., Stevens, R., Waters, P. J., Ryan, S., McDonald, D., et al. (2003) Hum. Mutat. 21, 333-344. - PubMed
-
- de la Cruz, F. & Koch, R. (2001) Clin. Perinatol. 28, 419-424. - PubMed
-
- Niederwieser, A. & Curtius, H. C. (1985) in Inherited Diseases of Amino Acid Metabolism, eds. Bickel, H. & Wachtel, U. (Georg Thieme, Stuttgart), pp. 104-121.
-
- Kure, S., Hou, D. C., Ohura, T., Iwamoto, H., Suzuki, S., Sugiyama, N., Sakamoto, O., Fujii, K., Matsubara, Y. & Narisawa, K. (1999) J. Pediatr. 135, 375-378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

