Long-term control of Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection in the absence of Toll-like receptors (TLRs): investigation of TLR2-, TLR6-, or TLR2-TLR4-deficient mice
- PMID: 15557622
- PMCID: PMC529115
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.12.6994-7004.2004
Long-term control of Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection in the absence of Toll-like receptors (TLRs): investigation of TLR2-, TLR6-, or TLR2-TLR4-deficient mice
Abstract
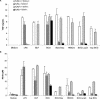
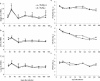
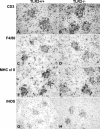
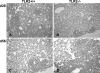
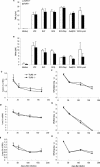
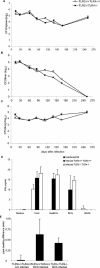
Live mycobacteria have been reported to signal through both Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR4 in vitro. Here, we investigated the role of TLR2 in the long-term control of the infection by the attenuated Mycobacterium, Mycobacterium bovis BCG, in vivo. We sought to determine whether the reported initial defect of bacterial control (K. A. Heldwein et al., J. Leukoc. Biol. 74:277-286, 2003) resolved in the chronic phase of BCG infection. Here we show that TLR2-deficient mice survived a 6-month infection period with M. bovis BCG and were able to control bacterial growth. Granuloma formation, T-cell and macrophage recruitment, and activation were normal. Furthermore, the TLR2 coreceptor, TLR6, is also not required since TLR6-deficient mice were able to control chronic BCG infection. Finally, TLR2-TLR4-deficient mice infected with BCG survived the 8-month observation period. Interestingly, the adaptive response of TLR2- and/or TLR4-deficient mice seemed essentially normal on day 14 or 56 after infection, since T cells responded normally to soluble BCG antigens. In conclusion, our data demonstrate that TLR2, TLR4, or TLR6 are redundant for the control of M. bovis BCG mycobacterial infection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor signaling in anti-cancer immunity.J Med Invest. 2003 Feb;50(1-2):9-24. J Med Invest. 2003. PMID: 12630564
-
Human toll-like receptors mediate cellular activation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Immunol. 1999 Oct 1;163(7):3920-7. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10490993
-
Synergism of toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), TLR4, and TLR6 ligation on the production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha in a spontaneous arthritis animal model of interleukin (IL)-1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice.Immunol Lett. 2009 Apr 27;123(2):138-43. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2009.03.004. Epub 2009 Mar 21. Immunol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19428561
-
[Frontier of mycobacterium research--host vs. mycobacterium].Kekkaku. 2005 Sep;80(9):613-29. Kekkaku. 2005. PMID: 16245793 Japanese.
-
TLR2 but not TLR4 signalling is critically involved in the inhibition of IFN-gamma-induced killing of mycobacteria by murine macrophages.Scand J Immunol. 2007 Feb;65(2):148-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2006.01888.x. Scand J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17257219
Cited by
-
IL-21-induced Bepsilon cell apoptosis mediated by natural killer T cells suppresses IgE responses.J Exp Med. 2006 Dec 25;203(13):2929-37. doi: 10.1084/jem.20062206. Epub 2006 Dec 18. J Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 17178921 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptors in central nervous system glial inflammation and homeostasis.J Neurosci Res. 2006 Apr;83(5):711-30. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20767. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16541438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like receptors and leishmaniasis.Infect Immun. 2008 Mar;76(3):866-72. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01090-07. Epub 2007 Dec 10. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18070909 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Lipoarabinomannan and related glycoconjugates: structure, biogenesis and role in Mycobacterium tuberculosis physiology and host-pathogen interaction.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011 Nov;35(6):1126-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00276.x. Epub 2011 May 31. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21521247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal Models for Tuberculosis in Translational and Precision Medicine.Front Microbiol. 2017 May 4;8:717. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00717. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28522990 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abel, B., N. Thieblemont, V. J. Quesniaux, N. Brown, J. Mpagi, K. Miyake, F. Bihl, and B. Ryffel. 2002. Toll-like receptor 4 expression is required to control chronic Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in mice. J. Immunol. 169:3155-3162. - PubMed
-
- Aliprantis, A. O., R. B. Yang, M. R. Mark, S. Suggett, B. Devaux, J. D. Radolf, G. R. Klimpel, P. Godowski, and A. Zychlinsky. 1999. Cell activation and apoptosis by bacterial lipoproteins through Toll-like receptor-2. Science 285:736-739. - PubMed
-
- Brightbill, H. D., D. H. Libraty, S. R. Krutzik, R. B. Yang, J. T. Belisle, J. R. Bleharski, M. Maitland, M. V. Norgard, S. E. Plevy, S. T. Smale, P. J. Brennan, B. R. Bloom, P. J. Godowski, and R. L. Modlin. 1999. Host defense mechanisms triggered by microbial lipoproteins through Toll-like receptors. Science 285:732-736. - PubMed
-
- Bulut, Y., E. Faure, L. Thomas, O. Equils, and M. Arditi. 2001. Cooperation of Toll-like receptor 2 and 6 for cellular activation by soluble tuberculosis factor and Borrelia burgdorferi outer surface protein A lipoprotein: role of Toll-interacting protein and IL-1 receptor signaling molecules in Toll-like receptor 2 signaling. J. Immunol. 167:987-994. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

