Characterization of immunodominant and potentially protective epitopes of Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 outer membrane lipoprotein PlpE
- PMID: 15557652
- PMCID: PMC529155
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.12.7265-7274.2004
Characterization of immunodominant and potentially protective epitopes of Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 outer membrane lipoprotein PlpE
Abstract
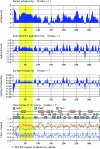
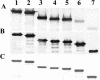
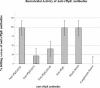
Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 (S1) is the most common bacterial isolate found in shipping fever pneumonia in beef cattle. Currently used vaccines against M. haemolytica do not provide complete protection against the disease. Research with M. haemolytica outer membrane proteins (OMPs) has shown that antibodies to one particular OMP from S1, PlpE, may be important in immunity. In a recently published work, members of our laboratory showed that recombinant PlpE (rPlpE) is highly immunogenic when injected subcutaneously into cattle and that the acquired immunity markedly enhanced resistance to experimental challenge (A. W. Confer, S. Ayalew, R. J. Panciera, M. Montelongo, L. C. Whitworth, and J. D. Hammer, Vaccine 21:2821-2829, 2003). The objective of this work was to identify epitopes of PlpE that are responsible for inducing the immune response. Western blot analysis of a series of rPlpE with nested deletions on both termini with bovine anti-PlpE hyperimmune sera showed that the immunodominant region is located close to the N terminus of PlpE. Fine epitope mapping, in which an array of overlapping 13-mer synthetic peptides attached to a derivatized cellulose membrane was probed with various affinity-purified anti-PlpE antibodies, identified eight highly reactive regions, of which region 2 (R2) was identified as the specific epitope. The R2 region is comprised of eight imperfect repeats of a hexapeptide (QAQNAP) and is located between residues 26 and 76. Complement-mediated bactericidal activity of affinity-purified anti-PlpE bovine antibodies confirmed that antibodies directed against the R2 region are effective in killing M. haemolytica.
Figures


References
-
- Al-Ghamdi, G. M., T. R. Ames, J. C. Baker, R. Walker, C. C. Chase, G. H. Frank, and S. K. Maheswaran. 2000. Serotyping of Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica isolates from the upper Midwest United States. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 12:576-578. - PubMed
-
- Aubry, P., L. D. Warnick, C. L. Guard, B. W. Hill, and M. F. Witt. 2001. Health and performance of young dairy calves vaccinated with a modified-live Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida vaccine. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 219:1739-1742. - PubMed
-
- Bakaletz, L. O., B. J. Kennedy, L. A. Novotny, G. Duquesne, J. Cohen, and Y. Lobet. 1999. Protection against development of otitis media induced by nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae by both active and passive immunization in a chinchilla model of virus-bacterium superinfection. Infect. Immun. 67:2746-2762. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakaletz, L. O., E. R. Leake, J. M. Billy, and P. T. Kaumaya. 1997. Relative immunogenicity and efficacy of two synthetic chimeric peptides of fimbrin as vaccinogens against nasopharyngeal colonization by nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in the chinchilla. Vaccine 15:955-961. - PubMed
-
- Blackwood, E. R., S. Ayalew, and A. W. Confer. 2002. Molecular and immunological analysis of the outer membrane protein, PlpE, from Mannheimia haemolytica serotypes 1, 2, and 6, abstr. 93P. In R. P. Ellis (ed.), Proceedings of the 83rd Annual Meeting of the Conference of Research Workers in Animal Diseases, St. Louis, Mo. Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

