Antifungal immune reactivity in nasal polyposis
- PMID: 15557653
- PMCID: PMC529139
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.12.7275-7281.2004
Antifungal immune reactivity in nasal polyposis
Abstract
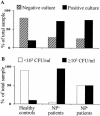
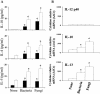
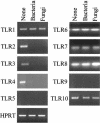
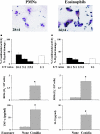
As a fungal etiology has been proposed to underlie severe nasal polyposis, the present study was undertaken to assess local antifungal immune reactivity in nasal polyposis. For this purpose, microbial colonization, along with the pattern of T helper 1 (Th1)/Th2 cytokine production and Toll-like receptor (TLR) expression, was evaluated in patients with nasal symptoms and with and without polyposis and in healthy subjects. The results show that Th2 reactivity was a common finding for patients with nasal polyposis regardless of the presence of microbes. The production of interleukin-10 was elevated in patients with bacterial and, particularly, fungal colonization, while both TLR2 expression and TLR4 expression were locally impaired in microbe-colonized patients. Eosinophils and neutrophils, highly recruited in nasal polyposis, were found to exert potent antifungal effector activities toward conidia and hyphae of the fungus and to be positively regulated by TLR2 or TLR4 stimulation. Therefore, a local imbalance between activating and deactivating signals to effector cells may likely contribute to fungal pathogenicity and the expression of local immune reactivity in nasal polyposis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Airborne fungi induce nasal polyp epithelial cell activation and Toll-like receptor expression.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010;153(1):46-52. doi: 10.1159/000301578. Epub 2010 Mar 31. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20357484
-
Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR4 are present inside human dendritic cells, associated with microtubules and the Golgi apparatus but are not detectable on the cell surface: integrity of microtubules is required for interleukin-12 production in response to internalized bacteria.Immunology. 2004 Feb;111(2):173-8. doi: 10.1111/j.0019-2805.2003.01803.x. Immunology. 2004. PMID: 15027902 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 2, 3, 4, 5 ligands and interleukin-4 synergistically induce TARC production in nasal polyp fibroblasts.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2008 Dec;35(4):515-20. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2008.02.001. Epub 2008 Mar 28. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2008. PMID: 18375080
-
Nasal polyposis: eosinophils and interleukin-5.Allergy. 1999 Jul;54(7):669-80. doi: 10.1034/j.1398-9995.1999.00095.x. Allergy. 1999. PMID: 10442522 Review. No abstract available.
-
Haemopoietic mechanisms in nasal polyposis and asthma.Thorax. 2000 Oct;55 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S24-5. doi: 10.1136/thorax.55.suppl_2.s24. Thorax. 2000. PMID: 10992551 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
TLR-2 expression and dysregulated human Treg/Th17 phenotype in Aspergillus flavus infected patients of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis.Microb Cell Fact. 2020 Nov 25;19(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01481-3. Microb Cell Fact. 2020. PMID: 33238997 Free PMC article.
-
Role of neutrophils in preventing and resolving acute fungal sinusitis.Infect Immun. 2007 Dec;75(12):5663-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01542-06. Epub 2007 Sep 17. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17875637 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives on the etiology of chronic rhinosinusitis: an immune barrier hypothesis.Am J Rhinol. 2008 Nov-Dec;22(6):549-59. doi: 10.2500/ajr.2008.22.3228. Epub 2008 Sep 10. Am J Rhinol. 2008. PMID: 18786300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in epithelial barrier function and host defense responses in chronic rhinosinusitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009 Jul;124(1):37-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.04.045. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19560577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different activations of toll-like receptors and antimicrobial peptides in chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyposis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jul;273(7):1779-88. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3816-1. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26518209
References
-
- Akdis, C. A., F. Kussebi, B. Pulendran, M. Akdis, R. P. Lauener, C. B. Schmidt-Weber, S. Klunker, G. Isitmangil, N. Hansjee, T. A. Wynn, S. Dillon, P. Erb, G. Baschang, K. Blaser, and S. S. Alkan. 2003. Inhibition of T helper 2-type responses, IgE production and eosinophilia by synthetic lipopeptides. Eur. J. Immunol. 33:2717-2726. - PubMed
-
- Akira, S. 2003. Mammalian Toll-like receptors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 15:5-11. - PubMed
-
- Arbour, N. C., E. Lorenz, B. C. Schutte, J. Zabner, J. N. Kline, M. Jones, K. Frees, J. L. Watt, and D. A. Schwartz. 2000. TLR4 mutations are associated with endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in humans. Nat. Genet. 25:187-191. - PubMed
-
- Bachert, C., P. Gevaert, G. Holtappels, C. Cuvelier, and P. van Cauwenberge. 2000. Nasal polyposis: from cytokines to growth. Am. J. Rhinol. 14:279-290. - PubMed
-
- Bateman, N. D., C. Fahy, and T. J. Woolford. 2003. Nasal polyps: still more questions than answers. J. Laryngol. Otol. 117:1-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

