Cleavage at the stem region releases an active ectodomain of the membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase
- PMID: 15560752
- PMCID: PMC1134979
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20041324
Cleavage at the stem region releases an active ectodomain of the membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase
Abstract
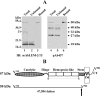
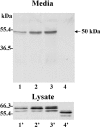
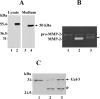
MT1-MMP (membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase) is a membrane-anchored MMP that can be shed to the extracellular milieu. In the present study we report the primary structure and activity of the major soluble form of MT1-MMP. MS analysis of the purified 50-kDa soluble MT1-MMP form shows that the enzyme extends from Tyr112 to Val524, indicating that formation of this species requires a proteolytic cleavage within the stem region. In agreement, deletion of the entire stem region of MT1-MMP inhibited shedding of the 50-kDa species. A recombinant 50-kDa species (Tyr112-Val524) expressed in cells exhibited enzymatic activity against pro-MMP-2 and galectin-3, and thus this species is a competent protease. The recombinant 50-kDa soluble form also decreased the level of surface-associated TIMP-2 (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2) when administered to cells expressing wild-type membrane-anchored MT1-MMP, suggesting that ectodomain shedding of MT1-MMP can alter the MMP/TIMP balance on the cell surface. A approximately 53-kDa species of MT1-MMP was also isolated from a non-detergent extract of human breast carcinoma tissue and was found to lack the cytosolic tail, as determined with specific MT1-MMP domain antibodies. Together, these data show that MT1-MMP ectodomain shedding is a physiological process that may broaden MT1-MMP activity to the pericellular space.
Figures

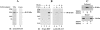

References
-
- Hotary K. B., Allen E. D., Brooks P. C., Datta N. S., Long M. W., Weiss S. J. Membrane type I matrix metalloproteinase usurps tumor growth control imposed by the three-dimensional extracellular matrix. Cell. 2003;114:33–45. - PubMed
-
- Ohuchi E., Imai K., Fujii Y., Sato H., Seiki M., Okada Y. Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase digests interstitial collagens and other extracellular matrix macromolecules. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:2446–2451. - PubMed
-
- Strongin A. Y., Collier I., Bannikov G., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Goldberg G. I. Mechanism of cell surface activation of 72-kDa type IV collagenase. Isolation of the activated form of the membrane metalloprotease. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:5331–5338. - PubMed
-
- Knauper V., Will H., Lopez-Otin C., Smith B., Atkinson S. J., Stanton H., Hembry R. M., Murphy G. Cellular mechanisms for human procollagenase-3 (MMP-13) activation. Evidence that MT1-MMP (MMP-14) and gelatinase a (MMP-2) are able to generate active enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:17124–17131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

