Incorporating social anxiety into a model of college student problematic drinking
- PMID: 15561454
- PMCID: PMC2684064
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2004.04.018
Incorporating social anxiety into a model of college student problematic drinking
Abstract
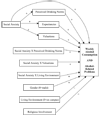
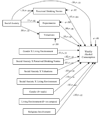
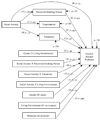
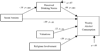
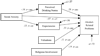
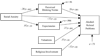
College problem drinking and social anxiety are significant public health concerns with highly negative consequences. College students are faced with a variety of novel social situations and situations encouraging alcohol consumption. The current study involved developing a path model of college problem drinking, including social anxiety, in 316 college students referred to an alcohol intervention due to a campus alcohol violation. Contrary to hypotheses, social anxiety generally had an inverse relationship with problem drinking. As expected, perceived drinking norms had important positive, direct effects on drinking variables. However, the results generally did not support the hypotheses regarding the mediating or moderating function of the valuations of expected effects and provided little support for the mediating function of alcohol expectancies in the relations among social anxiety and alcohol variables. Therefore, it seems that the influence of peers may be more important for college students than alcohol expectancies and valuations of alcohol's effects are. College students appear to be a unique population in respect to social anxiety and problem drinking. The implications of these results for college prevention and intervention programs were discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Social anxiety, alcohol expectancies, and self-efficacy as predictors of heavy drinking in college students.Addict Behav. 2006 Mar;31(3):388-98. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2005.05.020. Epub 2005 Jun 13. Addict Behav. 2006. PMID: 15951128
-
Social anxiety symptoms and drinking behaviors among college students: the mediating effects of drinking motives.Psychol Addict Behav. 2014 Sep;28(3):710-8. doi: 10.1037/a0036501. Epub 2014 May 19. Psychol Addict Behav. 2014. PMID: 24841178
-
Social anxiety and drinking in college students: a social cognitive theory analysis.Clin Psychol Rev. 1999 Aug;19(5):513-30. doi: 10.1016/s0272-7358(98)00058-0. Clin Psychol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10467489 Review.
-
Social anxiety and alcohol use: evaluation of the moderating and mediating effects of alcohol expectancies.J Anxiety Disord. 2004;18(1):33-49. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2003.07.005. J Anxiety Disord. 2004. PMID: 14725867
-
Peer influences on college drinking: a review of the research.J Subst Abuse. 2001;13(4):391-424. doi: 10.1016/s0899-3289(01)00098-0. J Subst Abuse. 2001. PMID: 11775073 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of underutilization of protective behavioral strategies in the relation of social anxiety with risky drinking.Addict Behav. 2020 Jan;100:106122. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.106122. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Addict Behav. 2020. PMID: 31610479 Free PMC article.
-
A longitudinal analysis of drinking motives moderating the negative affect-drinking association among college students.Psychol Addict Behav. 2010 Mar;24(1):38-47. doi: 10.1037/a0017530. Psychol Addict Behav. 2010. PMID: 20307111 Free PMC article.
-
Individual and Environmental Factors Associated with Tobacco Smoking, Alcohol Abuse and Illegal Drug Consumption in University Students: A Mediating Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Apr 27;17(9):3019. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17093019. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32349213 Free PMC article.
-
Social phobia in Nigerian university students: prevalence, correlates and co-morbidity.Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2009 Jun;44(6):458-63. doi: 10.1007/s00127-008-0457-3. Epub 2008 Oct 31. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2009. PMID: 18979054
-
College drinking problems and social anxiety: The importance of drinking context.Psychol Addict Behav. 2014 Jun;28(2):545-52. doi: 10.1037/a0035770. Psychol Addict Behav. 2014. PMID: 24955673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Addictive Behaviors Research Center. The Alcohol Skills Training Program facilitators manual. Psychology Department; University of Washington; 1997. Unpublished manual.
-
- Agnostinelli G, Brown JM, Miller WR. Effects of normative feedback on consumption among heavy drinking college students. Journal of Drug Education. 1995;25:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Aiken LS, West SG. Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications; 1991.
-
- Baer JS, Carey MM. Biases in the perceptions of the consequences of alcohol use among college students. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 1993;54:54–60. - PubMed
-
- Bandura A. Social learning theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall; 1977.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

