TMC125, a novel next-generation nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor active against nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1
- PMID: 15561844
- PMCID: PMC529207
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.12.4680-4686.2004
TMC125, a novel next-generation nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor active against nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1
Abstract
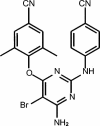
Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) are potent inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1); however, currently marketed NNRTIs rapidly select resistant virus, and cross-resistance within the class is extensive. A parallel screening strategy was applied to test candidates from a series of diarylpyrimidines against wild-type and resistant HIV strains carrying clinically relevant mutations. Serum protein binding and metabolic stability were addressed early in the selection process. The emerging clinical candidate, TMC125, was highly active against wild-type HIV-1 (50% effective concentration [EC50] = 1.4 to 4.8 nM) and showed some activity against HIV-2 (EC50 = 3.5 microM). TMC125 also inhibited a series of HIV-1 group M subtypes and circulating recombinant forms and a group O virus. Incubation of TMC125 with human liver microsomal fractions suggested good metabolic stability (15% decrease in drug concentration and 7% decrease in antiviral activity after 120 min). Although TMC125 is highly protein bound, its antiviral effect was not reduced by the presence of 45 mg of human serum albumin/ml, 1 mg of alpha1-acid glycoprotein/ml, or 50% human serum. In an initial screen for activity against a panel of 25 viruses carrying single and double reverse transcriptase amino acid substitutions associated with NNRTI resistance, the EC50 of TMC125 was <5 nM for 19 viruses, including the double mutants K101E+K103N and K103N+Y181C. TMC125 also retained activity (EC50 < 100 nM) against 97% of 1,081 recent clinically derived recombinant viruses resistant to at least one of the currently marketed NNRTIs. TMC125 is a potent next generation NNRTI, with the potential for use in individuals infected with NNRTI-resistant virus.
Figures
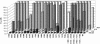
 , EC50 > 10 nM and < 100 nM; □, EC50 < 10 nM. NVP, nevirapine; DLV, delavirdine; EFV, efavirenz.
, EC50 > 10 nM and < 100 nM; □, EC50 < 10 nM. NVP, nevirapine; DLV, delavirdine; EFV, efavirenz.References
-
- Antinori, A., M. Zaccarelli, A. Cingolani, F. Forbici, M. G. Rizzo, M. P. Trotta, S. Di Giambenedetto, P. Narciso, A. Ammassari, E. Girardi, A. De Luca, and C. F. Perno. 2002. Cross-resistance among nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors limits recycling efavirenz after nevirapine failure. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 18:835-838. - PubMed
-
- Bacheler, L., S. Jeffrey, G. Hanna, R. D'Aquila, L. Wallace, K. Logue, B. Cordova, K. Hertogs, B. Larder, R. Buckery, D. Baker, K. Gallagher, H. Scarnati, R. Tritch, and C. Rizzo. 2001. Genotypic correlates of phenotypic resistance to efavirenz in virus isolates from patients failing nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor therapy. J. Virol. 75:4999-5008. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balotta, C., G. Facchi, M. Violin, S. Van Dooren, A. Cozzi-Lepri, F. Forbici, A. Bertoli, C. Riva, D. Senese, P. Caramello, G. Carnevale, G. Rizzardini, L. Cremonini, L. Monno, G. Rezza, C. F. Perno, G. Ippolito, A. d'Arminio-Monforte, A. M. Vandamme, and M. Moroni. 2001. Increasing prevalence of non-clade B HIV-1 strains in heterosexual men and women, as monitored by analysis of reverse transcriptase and protease sequences. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 27:499-505. - PubMed
-
- Bilello, J. A., P. A. Bilello, K. Stellrecht, J. Leonard, D. W. Norbeck, D. J. Kempf, T. Robins, and G. L. Drusano. 1996. Human serum alpha 1 acid glycoprotein reduces uptake, intracellular concentration, and antiviral activity of A-80987, an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 40:1491-1497. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bohets, H., K. Lavrijsen, J. Hendrickx, J. van Houdt, V. van Genechten, P. Verboven, W. Meuldermans, and J. Heykants. 2000. Identification of the cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the metabolism of cisapride: in vitro studies of potential co-medication interactions. Br. J. Pharmacol. 129:1655-1667. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

