A transcriptional profile of aging in the human kidney
- PMID: 15562319
- PMCID: PMC532391
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020427
A transcriptional profile of aging in the human kidney
Abstract
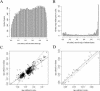
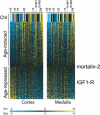
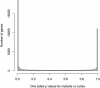
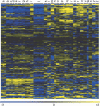
In this study, we found 985 genes that change expression in the cortex and the medulla of the kidney with age. Some of the genes whose transcripts increase in abundance with age are known to be specifically expressed in immune cells, suggesting that immune surveillance or inflammation increases with age. The age-regulated genes show a similar aging profile in the cortex and the medulla, suggesting a common underlying mechanism for aging. Expression profiles of these age-regulated genes mark not only age, but also the relative health and physiology of the kidney in older individuals. Finally, the set of aging-regulated kidney genes suggests specific mechanisms and pathways that may play a role in kidney degeneration with age.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures


References
-
- Droge W. Oxidative stress and aging. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;543:191–200. - PubMed
-
- Guarente L, Kenyon C. Genetic pathways that regulate ageing in model organisms. Nature. 2000;408:255–262. - PubMed
-
- Hasty P, Campisi J, Hoeijmakers J, van Steeg H, Vijg J. Aging and genome maintenance: Lessons from the mouse? Science. 2003;299:1355–1359. - PubMed
-
- Hekimi S, Guarente L. Genetics and the specificity of the aging process. Science. 2003;299:1351–1354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

