In vivo visualization of Alzheimer's amyloid plaques by magnetic resonance imaging in transgenic mice without a contrast agent
- PMID: 15562496
- PMCID: PMC2744889
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.20266
In vivo visualization of Alzheimer's amyloid plaques by magnetic resonance imaging in transgenic mice without a contrast agent
Abstract
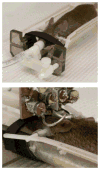
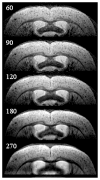
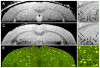
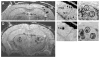
One of the cardinal pathologic features of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the formation of senile, or amyloid, plaques. Transgenic mice have been developed that express one or more of the genes responsible for familial AD in humans. Doubly transgenic mice develop "human-like" plaques, providing a mechanism to study amyloid plaque biology in a controlled manner. Imaging of labeled plaques has been accomplished with other modalities, but only MRI has sufficient spatial and contrast resolution to visualize individual plaques noninvasively. Methods to optimize visualization of plaques in vivo in transgenic mice at 9.4 T using a spin echo sequence based on adiabatic pulses are described. Preliminary results indicate that a spin echo acquisition more accurately reflects plaque size, while a T2* weighted gradient echo sequence reflects plaque iron content, not plaque size. In vivo MRI-ex vivo MRI-in vitro histologic correlations are provided. Histologically verified plaques as small as 50 microm in diameter were visualized in living animals. To our knowledge this work represents the first demonstration of noninvasive in vivo visualization of individual AD plaques without the use of a contrast agent.
Figures



References
-
- Evans DA, Funkenstein HH, Albert MS. Prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease in a community population of older persons. JAMA. 1989;262:2551–2556. - PubMed
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1984;34:939–944. - PubMed
-
- Growdon JH. Biomarkers of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 1999;56:281–283. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Hsiao K, Chapman P, Nilsen S, Eckman C, Harigaya Y, Younkin D, Yang F, Cole GM. Correlative memory deficits, Aβ elevation, and amyloid plaques in transgenic mice. Science. 1996;274:99–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

