Molecular characterization of radial spoke subcomplex containing radial spoke protein 3 and heat shock protein 40 in sperm flagella of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis
- PMID: 15563603
- PMCID: PMC545899
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0784
Molecular characterization of radial spoke subcomplex containing radial spoke protein 3 and heat shock protein 40 in sperm flagella of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis
Abstract
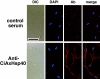
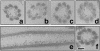
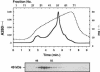
Members of the heat-shock protein (HSP)40 regulate the protein folding activity of HSP70 proteins and help the functional specialization of this molecular chaperone system in various types of cellular events. We have recently identified Hsp40 as a component of flagellar axoneme in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis, suggesting a correlation between Hsp40 related chaperone system and flagellar function. In this study, we have found that Ciona 37-kDa Hsp40 is extracted from KCl-treated axonemes with 0.5 M KI solution and comigrates with radial spoke protein (RSP)3 along with several proteins as a complex through gel filtration and ion exchange columns. Peptide mass fingerprinting with matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization/time of flight/mass spectrometry revealed that other proteins in the complex include a homolog of sea urchin spokehead protein (homolog of RSP4/6), a membrane occupation and recognition nexus repeat protein with sequence similarity with meichroacidin, and a functionally unknown 33-kDa protein. A spoke head protein, LRR37, is not included in the complex, suggesting that the complex constructs the stalk of radial spoke. Immunoelectron microscopy indicates that Hsp40 is localized in the distal portion of spoke stalk, possibly at the junction between spoke head and the stalk.
Figures


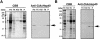


Similar articles
-
Identification of a novel leucine-rich repeat protein as a component of flagellar radial spoke in the Ascidian Ciona intestinalis.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Feb;14(2):774-85. doi: 10.1091/mbc.02-06-0089. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12589069 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic characterization of sperm radial spokes identifies a novel spoke protein with an ubiquitin domain.FEBS Lett. 2009 Jul 7;583(13):2201-7. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.06.016. Epub 2009 Jun 13. FEBS Lett. 2009. PMID: 19527718
-
Dimeric novel HSP40 is incorporated into the radial spoke complex during the assembly process in flagella.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Feb;16(2):637-48. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0787. Epub 2004 Nov 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15563613 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of sperm flagellar axonemes: structural and evolutionary aspects.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Apr;1101:506-26. doi: 10.1196/annals.1389.017. Epub 2007 Mar 15. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17363437 Review.
-
Not all J domains are created equal: implications for the specificity of Hsp40-Hsp70 interactions.Protein Sci. 2005 Jul;14(7):1697-709. doi: 10.1110/ps.051406805. Protein Sci. 2005. PMID: 15987899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radial Spokes-A Snapshot of the Motility Regulation, Assembly, and Evolution of Cilia and Flagella.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017 May 1;9(5):a028126. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028126. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017. PMID: 27940518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of a flagellar HSP40 ensuring rhythmic beating.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Jan 15;30(2):228-241. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-01-0047. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30427757 Free PMC article.
-
A Toxoplasma MORN1 null mutant undergoes repeated divisions but is defective in basal assembly, apicoplast division and cytokinesis.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 19;5(8):e12302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012302. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20808817 Free PMC article.
-
Rare Human Diseases: Model Organisms in Deciphering the Molecular Basis of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia.Cells. 2019 Dec 11;8(12):1614. doi: 10.3390/cells8121614. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31835861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct architecture and composition of mouse axonemal radial spoke head revealed by cryo-EM.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 26;118(4):e2021180118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2021180118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34871179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berruti, G., and Martegani, E. (2001). MSJ-1, a mouse testis-specific DnaJ protein, is highly expressed in haploid male germ cells and interacts with the testis-specific heatshock protein Hsp70-2. Biol. Reprod. 65, 488-495. - PubMed
-
- Bloch, M. A., and Johnson, K. A. (1995). Identification of a molecular chaperone in the eukaryotic flagellum and its localization to the site of microtubule assembly. J. Cell Sci. 108, 3541-3545. - PubMed
-
- Casano, C., Gianguzza, F., Roccheri, M. C., Di Giorgi, R., Maenza, L., and Ragusa, M. A. (2003). Hsp40 is involved in cilia regeneration in sea urchin embryos. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 51, 1581-1587. - PubMed
-
- Dehal, P., et al., (2002). The draft genome of Ciona intestinalis: insights into chordate and vertebrate origins. Science 298, 2157-2167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

