Design of a real time quantitative PCR assay to assess global mRNA amplification of small size specimens for microarray hybridisation
- PMID: 15563668
- PMCID: PMC1770498
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2004.017988
Design of a real time quantitative PCR assay to assess global mRNA amplification of small size specimens for microarray hybridisation
Abstract
Background: Low RNA yields from clinical samples are a limiting step for microarray technology.
Aims: To design an accurate real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay to assess the crucial step of global mRNA amplification performed before microarray hybridisation, using less than 1 microg total RNA.
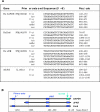
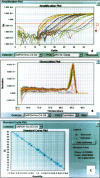
Methods: Three RNA extraction procedures were compared for small size samples. Total RNA was amplified from universal RNA or the BC-H1 breast cancer micrometastatic cell line using three different protocols. Real time quantitative PCR technology was used for accurate measurement of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor and cytokeratin 8 RNA amplification rates and ratios, using primer sets binding at various distances from the 3' end of transcripts. A 50 mer oligomeric array targeting 87 genes potentially involved in breast cancer metastatic progression was built and hybridised with amplified RNA.
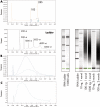
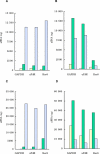
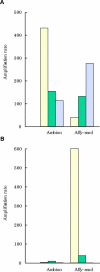
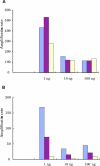
Results: Eighteen nanograms of total RNA could be purified from 1000 BC-H1 micrometastatic cells. Amplification rates of 25,000 to 100,000 were achieved with as little as 10 ng of starting material. However, results were highly variable, depending on the amount of starting material, gene characteristics, sample quality, and protocols used. Oligomeric array hybridisation with 20 microg reference RNA resulted in specific and reproducible signals for 83% of the genes, whereas mRNA amplification from less than 400 ng of starting material resulted in selective detection of signals from highly expressed genes.
Conclusions: Improvements in the design of global mRNA amplification procedures and oligomeric arrays are needed to extract informative gene expression data from clinical samples containing limited cell numbers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An alternative method to amplify RNA without loss of signal conservation for expression analysis with a proteinase DNA microarray in the ArrayTube format.BMC Genomics. 2006 Jun 12;7:144. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-144. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16768788 Free PMC article.
-
[Use of the real-time RT-PCR method for investigation of small stable RNA expression level in human epidermoid carcinoma cells A431].Tsitologiia. 2003;45(4):392-402. Tsitologiia. 2003. PMID: 14520871 Russian.
-
Comparative analysis of a 3' end tag PCR and a linear RNA amplification approach for microarray analysis.J Biotechnol. 2007 Jan 20;127(4):638-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.08.016. Epub 2006 Sep 25. J Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 16997411
-
[Quantitative PCR in the diagnosis of Leishmania].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):163-7. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305709 Review. Italian.
-
RNA amplification strategies for small sample populations.Methods. 2005 Nov;37(3):229-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2005.09.003. Methods. 2005. PMID: 16308152 Review.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000;406:747–52. - PubMed
-
- van ’t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, et al. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 2002;415:530–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
