Lytic cycle gene regulation of Epstein-Barr virus
- PMID: 15564457
- PMCID: PMC533939
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.24.13460-13469.2004
Lytic cycle gene regulation of Epstein-Barr virus
Abstract
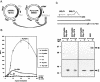
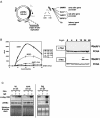
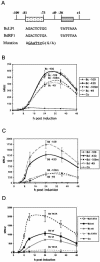
Episomal reporter plasmids containing the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) oriP sequence stably transfected into Akata Burkitt's lymphoma cells were used to analyze EBV lytic cycle gene regulation. First, we found that the Zp promoter of EBV, but not the Rp promoter, can be activated in the absence of protein synthesis in these oriP plasmids, casting doubt on the immediate early status of Rp. An additional level of regulation of Zp was implied by analysis of a mutation of the ZV element. Second, our analysis of late lytic cycle promoters revealed that the correct relative timing, dependence on ori lyt in cis, and sensitivity to inhibitors of DNA replication were reconstituted on the oriP plasmids. Late promoter luciferase activity from oriP plasmids also incorporating replication-competent ori lyt was phosphonoacetic acid sensitive, a hallmark of EBV late genes. A minimal ori lyt, which only replicates weakly, was sufficient to confer late timing of expression specifically on late promoters. Finally, deletion analysis of EBV late promoter sequences upstream of the transcription start site confirmed that sequences between -49 and +30 are sufficient for late gene expression, which is dependent on ori lyt in cis. However, the TATT version of the TATA box found in many late genes was not essential for late expression.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

