Furin-mediated cleavage of the feline foamy virus Env leader protein
- PMID: 15564468
- PMCID: PMC533928
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.24.13573-13581.2004
Furin-mediated cleavage of the feline foamy virus Env leader protein
Abstract
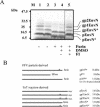
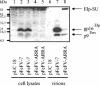
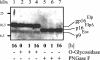
The molecular biology of spuma or foamy retroviruses is different from that of the other members of the Retroviridae. Among the distinguishing features, the N-terminal domain of the foamy virus Env glycoprotein, the 16-kDa Env leader protein Elp, is a component of released, infectious virions and is required for particle budding. The transmembrane protein Elp specifically interacts with N-terminal Gag sequences during morphogenesis. In this study, we investigate the mechanism of Elp release from the Env precursor protein. By a combination of genetic, biochemical, and biophysical methods, we show that the feline foamy virus (FFV) Elp is released by a cellular furin-like protease, most likely furin itself, generating an Elp protein consisting of 127 amino acid residues. The cleavage site fully conforms to the rules for an optimal furin site. Proteolytic processing at the furin cleavage site is required for full infectivity of FFV. However, utilization of other furin proteases and/or cleavage at a suboptimal signal peptidase cleavage site can partially rescue virus viability. In addition, we show that FFV Elp carries an N-linked oligosaccharide that is not conserved among the known foamy viruses.
Figures




References
-
- Alke, A., A. Schwantes, K. Kido, M. Flötenmeyer, R. M. Flügel, and M. Löchelt. 2001. The bet gene of feline foamy virus is required for virus replication. Virology 287:310-320. - PubMed
-
- Alke, A., A. Schwantes, M. Zemba, R. M. Flügel, and M. Löchelt. 2000. Characterization of the humoral immune response and virus replication in cats experimentally infected with feline foamy virus. Virology 275:170-176. - PubMed
-
- Basak, A., M. Zhong, J. Munzer, M. Chretien, and N. Seidah. 2001. Implication of the proprotein convertases furin, PC5 and PC7 in the cleavage of surface glycoproteins of Hong Kong, Ebola and respiratory syncytial viruses: a comparative analysis with fluorogenic peptides. Biochem. J. 353:537-545. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bornsen, K. 2000. Influence of salts, buffers, detergents, solvents, and matrices on MALDI-MS protein analysis in complex mixtures. Methods Mol. Biol. 146:387-404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

