Neutralization profiles of newly transmitted human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by monoclonal antibodies 2G12, 2F5, and 4E10
- PMID: 15564511
- PMCID: PMC533925
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.24.14039-14042.2004
Neutralization profiles of newly transmitted human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by monoclonal antibodies 2G12, 2F5, and 4E10
Abstract
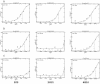
As the AIDS epidemic continues unabated, the development of a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) vaccine is critical. Ideally, an effective vaccine should elicit cell-mediated and neutralizing humoral immune responses. We have determined the in vitro susceptibility profile of sexually transmitted viruses from 91 patients with acute and early HIV-1 infection to three monoclonal antibodies, 2G12, 2F5, and 4E10. Using a recombinant virus assay to measure neutralization, we found all transmitted viruses were neutralized by 4E10, 80% were neutralized by 2F5, and only 37% were neutralized by 2G12. We propose that the induction of 4E10-like antibodies should be a priority in designing immunogens to prevent HIV-1 infection.
Figures
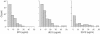
References
-
- Armbruster, C., G. M. Stiegler, B. A. Vcelar, W. Jager, N. L. Michael, N. Vetter, and H. W. Katinger. 2002. A phase I trial with two human monoclonal antibodies (hMAb 2F5, 2G12) against HIV-1. AIDS 16:227-233. - PubMed
-
- Burton, D. R., R. C. Desrosiers, R. W. Doms, W. C. Koff, P. D. Kwong, J. P. Moore, G. J. Nabel, J. Sodroski, I. A. Wilson, and R. T. Wyatt. 2004. HIV vaccine design and the neutralizing antibody problem. Nat. Immunol. 5:233-236. - PubMed
-
- Calarese, D. A., C. N. Scanlan, M. B. Zwick, S. Deechongkit, Y. Mimura, R. Kunert, P. Zhu, M. R. Wormald, R. L. Stanfield, K. H. Roux, J. W. Kelly, P. M. Rudd, R. A. Dwek, H. Katinger, D. R. Burton, and I. A. Wilson. 2003. Antibody domain exchange is an immunological solution to carbohydrate cluster recognition. Science 300:2065-2071. - PubMed
-
- Cardosa, R., M. B. Zwick, R. Kunert, H. Katinger, D. R. Burton, and I. A. Wilson. 2003. Structural insights for 4E10 antibody neutralization on HIV-1. AIDS Vaccine 2003, New York, N.Y. [Online.] http://www.aidsvaccine2003.org.
-
- Conley, A. J., J. A. Kessler II, L. J. Boots, P. M. McKenna, W. A. Schleif, E. A. Emini, G. E. Mark III, H. Katinger, E. K. Cobb, S. M. Lunceford, S. R. Rouse, and K. K. Murthy. 1996. The consequence of passive administration of an anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralizing monoclonal antibody before challenge of chimpanzees with a primary virus isolate. J. Virol. 70:6751-6758. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

