Genetic screen for monitoring severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3C-like protease
- PMID: 15564515
- PMCID: PMC533918
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.24.14057-14061.2004
Genetic screen for monitoring severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3C-like protease
Abstract
A novel coronavirus (SCoV) is the etiological agent of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Site-specific proteolysis plays a critical role in regulating a number of cellular and viral processes. Since the main protease of SCoV, also termed 3C-like protease, is an attractive target for drug therapy, we have developed a safe, simple, and rapid genetic screen assay to monitor the activity of the SCoV 3C-like protease. This genetic system is based on the bacteriophage lambda regulatory circuit, in which the viral repressor cI is specifically cleaved to initiate the lysogenic-to-lytic switch. A specific target for the SCoV 3C-like protease, P1/P2 (SAVLQ/SGFRK), was inserted into the lambda phage cI repressor. The target specificity of the SCoV P1/P2 repressor was evaluated by coexpression of this repressor with a chemically synthesized SCoV 3C-like protease gene construct. Upon infection of Escherichia coli cells containing the two plasmids encoding the cI. SCoV P1/P2-cro and the beta-galactosidase-SCoV 3C-like protease constructs, lambda phage replicated up to 2,000-fold more efficiently than in cells that did not express the SCoV 3C-like protease. This simple and highly specific assay can be used to monitor the activity of the SCoV 3C-like protease, and it has the potential to be used for screening specific inhibitors.
Figures

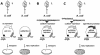

References
-
- Anand, K., J. Ziebuhr, P. Wadhwani, J. R. Mesters, and R. Hilgenfeld. 2003. Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science 300:1763-1767. - PubMed
-
- Cabana, M., G. Fernandez, M. Parera, B. Clotet, and M. A. Martinez. 2002. Catalytic efficiency and phenotype of HIV-1 proteases encoding single critical resistance substitutions. Virology 300:71-78. - PubMed
-
- Cello, J., A. V. Paul, and E. Wimmer. 2002. Chemical synthesis of poliovirus cDNA: generation of infectious virus in the absence of natural template. Science 297:1016-1018. - PubMed
-
- Drosten, C., S. Gunther, W. Preiser, S. van der Werf, H. R. Brodt, S. Becker, H. Rabenau, M. Panning, L. Kolesnikova, R. A. Fouchier, A. Berger, A. M. Burguiere, J. Cinatl, M. Eickmann, N. Escriou, K. Grywna, S. Kramme, J. C. Manuguerra, S. Muller, V. Rickerts, M. Sturmer, S. Vieth, H. D. Klenk, A. D. Osterhaus, H. Schmitz, and H. W. Doerr. 2003. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 348:1967-1976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

