Ethanol potentiation of GABAergic synaptic transmission may be self-limiting: role of presynaptic GABA(B) receptors
- PMID: 15564584
- PMCID: PMC6730127
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1768-04.2004
Ethanol potentiation of GABAergic synaptic transmission may be self-limiting: role of presynaptic GABA(B) receptors
Abstract
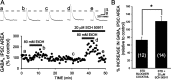
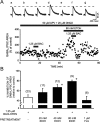
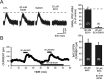
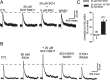
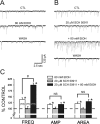
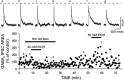
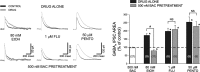
Ethanol enhances GABAergic synaptic inhibition, and this interaction contributes to many of the behavioral and cognitive effects of this drug. Most studies suggest that ethanol enhances GABAergic neurotransmission via an allosteric potentiation of the postsynaptic GABA(A) receptors that mediate fast synaptic inhibition in the mammalian CNS. Despite widespread acceptance of this hypothesis, direct support for such a mechanism has been difficult to obtain. Ethanol does not enhance GABA(A) receptor function in all brain regions or under all experimental conditions, and factors responsible for this variability remain mostly unknown. Notably, blockade of GABA(B) receptors dramatically enhances ethanol potentiation of hippocampal GABA(A) IPSPs and IPSCs, suggesting that some unknown GABA(B) receptor mechanism limits the overall potentiating effect of ethanol on GABAergic synapses. In this study, we demonstrate that, at perisomatic synapses in the rat hippocampus, ethanol enhances presynaptic GABA(B) autoreceptor function and that this interaction reduces the overall potentiating effect of ethanol at these synapses. We further show that ethanol significantly elevates basal presynaptic GABA(B) receptor tone, possibly via an increase in spontaneous GABA release, and that pretreatment with a subthreshold concentration of the GABA(B) receptor agonist baclofen blocks ethanol but not flunitrazepam or pentobarbital potentiation of GABA(A) IPSCs. These data suggest that an interaction between ethanol and presynaptic GABA(B) autoreceptor activity regulates the ethanol sensitivity of GABAergic synapses. Given that the in vitro ethanol sensitivity of these synapses correlates with in vivo ethanol responsiveness in a number of rodent lines, our data further suggest that presynaptic GABA(B) receptor activity may play a role in regulating behavioral sensitivity to ethanol.
Figures
References
-
- Bowery NG, Enna SJ (2000) Gamma-aminobutyric acid(B) receptors: first of the functional metabotropic heterodimers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 292: 2-7. - PubMed
-
- Couve A, Moss SJ, Pangalos MN (2000) GABAB receptors: a new paradigm in G protein signaling. Mol Cell Neurosci 16: 296-312. - PubMed
-
- Crowder TL, Ariwodola OJ, Weiner JL (2002) Ethanol antagonizes kainate receptor-mediated inhibition of evoked GABA(A) inhibitory postsynaptic currents in the rat hippocampal CA1 region. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303: 937-944. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
