Decreased synaptic activity shifts the calcium dependence of release at the mammalian neuromuscular junction in vivo
- PMID: 15564585
- PMCID: PMC6730126
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2755-04.2004
Decreased synaptic activity shifts the calcium dependence of release at the mammalian neuromuscular junction in vivo
Abstract
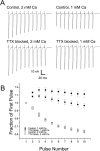
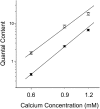
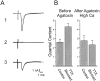
We examined the mechanism underlying increased quantal content after block of activity at the mouse neuromuscular junction in vivo. We found that, when quantal content was measured in solution containing normal extracellular calcium, block of activity had no effect on either quantal content or the response to repetitive stimulation. However, when quantal content was measured in low extracellular calcium, there was a large increase in quantal content after block of activity. The increase in quantal content was accompanied by increased depression during repetitive stimulation. The explanation for these findings was that there was a shift in the calcium dependence of release after block of activity that manifested as an increase in probability of release in low extracellular calcium. Block of presynaptic P/Q channels eliminated the increase in probability of release. We propose that activity-dependent regulation of presynaptic calcium entry may contribute to homeostatic regulation of quantal content.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Calcium channels coupled to neurotransmitter release at dually innervated neuromuscular junctions in the newborn rat.Neuroscience. 2001;102(3):697-708. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00507-8. Neuroscience. 2001. PMID: 11226706
-
Calcium channels coupled to neurotransmitter release at neonatal rat neuromuscular junctions.J Physiol. 1999 Jan 15;514 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):533-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.533ae.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 9852333 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Ca2+ channel blocker neurotoxins on transmitter release and presynaptic currents at the mouse neuromuscular junction.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Aug;121(8):1531-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701290. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9283685 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling of L-type calcium channels to neurotransmitter release at mouse motor nerve terminals.Pflugers Arch. 2001 Mar;441(6):824-31. doi: 10.1007/s004240000489. Pflugers Arch. 2001. PMID: 11316267
-
Calcium channels in the neuromuscular junction.Int Rev Cytol. 1993;147:193-232. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60769-x. Int Rev Cytol. 1993. PMID: 8225834 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Temporal requirement for high SMN expression in SMA mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Sep 15;20(18):3578-91. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr275. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21672919 Free PMC article.
-
The Neuromuscular Junction: Aging at the Crossroad between Nerves and Muscle.Front Aging Neurosci. 2014 Aug 11;6:208. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00208. eCollection 2014. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25157231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct roles for motor neuron autophagy early and late in the SOD1G93A mouse model of ALS.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Sep 26;114(39):E8294-E8303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1704294114. Epub 2017 Sep 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28904095 Free PMC article.
-
ACh Transfers: Homeostatic Plasticity of Cholinergic Synapses.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Mar;43(2):697-709. doi: 10.1007/s10571-022-01227-2. Epub 2022 May 28. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 35643882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MuSK Regulates Neuromuscular Junction Nav1.4 Localization and Excitability.J Neurosci. 2025 Apr 9;45(15):e1279232025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1279-23.2025. J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39880682
References
-
- Argentieri TM, Aiken SP, Laxminarayan S, McArdle JJ (1992) Characteristics of synaptic transmission in reinnervating rat skeletal muscle. Pflügers Arch 421: 256-261. - PubMed
-
- Atwood HL, Karunanithi S (2002) Diversification of synaptic strength: presynaptic elements. Nat Rev Neurosci 3: 497-516. - PubMed
-
- Barstad JA, Lilleheil G (1968) Transversely cut diaphragm preparation from rat. An adjuvant tool in the study of the physiology and pharmacology of the myoneural junction. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 175: 373-390. - PubMed
-
- Burrone J, Murthy VN (2003) Synaptic gain control and homeostasis. Curr Opin Neurobiol 13: 560-567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
