Activation of the cGMP pathway in dopaminergic structures reduces cocaine-induced EGR-1 expression and locomotor activity
- PMID: 15564589
- PMCID: PMC6730124
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1398-04.2004
Activation of the cGMP pathway in dopaminergic structures reduces cocaine-induced EGR-1 expression and locomotor activity
Abstract
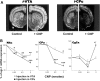
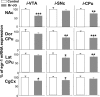
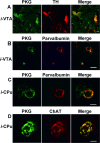
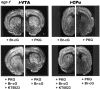
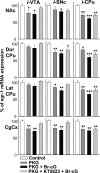
Nitric oxide (NO) and the C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) exert their action on brain via the cGMP signaling pathway. NO, by activating soluble guanylyl cyclase, and CNP, by stimulating membrane-bound guanylyl cyclase, cause intracellular increases of cGMP, activating cGMP-dependent protein kinases (PKGs). We show here that injection of CNP into the rat ventral tegmental area strongly reduced cocaine-induced egr-1 expression in the nucleus accumbens in a dose-dependent manner. The effect of CNP was reversed by the previous injection of a selective PKG inhibitor, KT5823. Activation of PKG by 8-bromo-cGMP reduced, like CNP, cocaine-induced gene transcription in dopaminergic structures. To confirm the involvement of PKG, this was overexpressed in either the mesencephalon or the caudate-putamen. Using the polyethyleneimine delivery system, an active protein was expressed by injecting a plasmid vector containing the human PKG-Ialpha cDNA. PKG was overexpressed in dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons when the plasmid was injected in the ventral tegmental area, whereas overexpression was observed in medium spiny GABAergic neurons and in both cholinergic and GABAergic interneurons when the PKG vector was injected into the caudate-putamen. Activation of the overexpressed PKG reduced cocaine-induced egr-1 expression in dopaminergic structures and affected behavior (i.e., locomotor activity). These effects were again reversed by previous injection of the selective PKG inhibitor. The current data suggest that NO and the neuropeptide CNP are potential regulators of cocaine-related effects on behavior.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Overexpression of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase reduces MeCP2 and HDAC2 expression.Brain Behav. 2012 Nov;2(6):732-40. doi: 10.1002/brb3.92. Epub 2012 Sep 17. Brain Behav. 2012. PMID: 23170236 Free PMC article.
-
C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) regulates cocaine-induced dopamine increase and immediate early gene expression in rat brain.Eur J Neurosci. 2001 Nov;14(10):1702-8. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01791.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11860464
-
The receptor attributable to C-type natriuretic peptide-induced differentiation of osteoblasts is switched from type B- to type C-natriuretic peptide receptor with aging.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Feb 15;103(3):753-64. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21448. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 17562543
-
Involvement of cyclic GMP and protein kinase G in the regulation of apoptosis and survival in neural cells.Neurosignals. 2002 Jul-Aug;11(4):175-90. doi: 10.1159/000065431. Neurosignals. 2002. PMID: 12393944 Review.
-
Cyclic GMP and protein kinase-G in myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion: opportunities and obstacles for survival signaling.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Nov;152(6):855-69. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707409. Epub 2007 Aug 13. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17700722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Up-regulation of microglial CD11b expression by nitric oxide.J Biol Chem. 2006 May 26;281(21):14971-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600236200. Epub 2006 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16551637 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of glial fibrillary acidic protein expression in astrocytes by nitric oxide.J Neurosci. 2006 May 3;26(18):4930-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5480-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16672668 Free PMC article.
-
PKG and PKA signaling in LTP at GABAergic synapses.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 Jun;34(7):1829-42. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.5. Epub 2009 Feb 4. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19194373 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleosome Repositioning: A Novel Mechanism for Nicotine- and Cocaine-Induced Epigenetic Changes.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 28;10(9):e0139103. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139103. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26414157 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D4 receptors linked to protein kinase G are required for changes in dopamine release followed by locomotor activity after repeated cocaine administration.Exp Brain Res. 2015 May;233(5):1511-8. doi: 10.1007/s00221-015-4228-6. Epub 2015 Feb 22. Exp Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25702161
References
-
- Ariano MA (1983) Distribution of components of the guanosine 3′,5′-phosphate system in rat caudate-putamen. Neuroscience 10: 707-723. - PubMed
-
- Babinski K, Haddad P, Vallerand D, McNicoll N, de Lean A, Ong H (1995) Natriuretic peptides inhibit nicotine-induced whole-cell currents and catecholamine secretion in bovine chromaffin cells: evidence for the involvement of the atrial natriuretic factor R2 receptors. J Neurochem 64: 1080-1087. - PubMed
-
- Bhat RV, Baraban JM (1993) Activation of transcription factor genes in striatum by cocaine: role of both serotonin and dopamine systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267: 496-505. - PubMed
-
- Bonkale WL, Cowburn RF, Winblad B, Fastbom J (1997) Autoradiographic characterization of [3H]cGMP binding sites in the rat brain. Brain Res 763: 1-13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
