A role of ventral tegmental area glutamate in contextual cue-induced relapse to heroin seeking
- PMID: 15564590
- PMCID: PMC6730135
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3207-04.2004
A role of ventral tegmental area glutamate in contextual cue-induced relapse to heroin seeking
Abstract
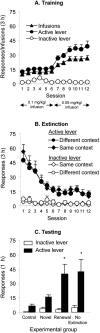
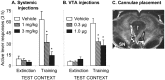
The environmental context previously associated with opiate use plays an important role in human relapse, but the neuronal mechanisms involved in context-induced drug relapse are not known. Using a rat relapse model, we determined the effect of a group II metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist [LY379268 ((-)-2-oxa-4-aminobicylco hexane-4,6-dicarboxylic acid)] on contextual cue-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. LY379268, which acts centrally to reduce evoked glutamate release, was injected systemically or directly into the ventral tegmental area (VTA), a brain area involved in opiate reward and conditioned drug effects. Rats were trained to self-administer intravenous heroin for 12 d; drug infusions were paired with a discrete tone-light cue. Subsequently, lever pressing was extinguished in the presence of the discrete cue in a context that differed from the drug self-administration context in terms of visual, auditory, tactile, and circadian cues. After extinction of lever responding, LY379268 was injected systemically or into the VTA, and nonreinforced responding was determined in the extinction context or the drug context. Exposure to the heroin-associated context induced robust reinstatement of drug seeking, and this effect was attenuated by systemic or intra-VTA injections of LY379268. Results indicate that glutamate transmission in the VTA plays an important role in contextual cue-induced relapse to heroin seeking.
Figures
References
-
- Bechara A, Nader K, van der Kooy D (1998) A two-separate-motivational-systems hypothesis of opioid addiction. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59: 1-17. - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME (2002) Context, ambiguity, and unlearning: sources of relapse after behavioral extinction. Biol Psychiatry 52: 976-986. - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME, Bolles RC (1979) Contextual control of the extinction of conditioned fear. Learn Motiv 10: 445-466.
-
- Byrne R, Harris G, Aston-Jones G (2003) Glutamate input to the ventral tegmental area is necessary for both learning and expression of morphine place preference. Soc Neurosci Abstr 29: 110.1.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
