Crystal structure of a PIWI protein suggests mechanisms for siRNA recognition and slicer activity
- PMID: 15565169
- PMCID: PMC535097
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600488
Crystal structure of a PIWI protein suggests mechanisms for siRNA recognition and slicer activity
Abstract
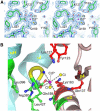
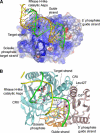
RNA silencing regulates gene expression through mRNA degradation, translation repression and chromatin remodelling. The fundamental engines of RNA silencing are RISC and RITS complexes, whose common components are 21-25 nt RNA and an Argonaute protein containing a PIWI domain of unknown function. The crystal structure of an archaeal Piwi protein (AfPiwi) is organised into two domains, one resembling the sugar-binding portion of the lac repressor and another with similarity to RNase H. Invariant residues and a coordinated metal ion lie in a pocket that surrounds the conserved C-terminus of the protein, defining a key functional region in the PIWI domain. Furthermore, two Asp residues, conserved in the majority of Argonaute sequences, align spatially with the catalytic Asp residues of RNase H-like catalytic sites, suggesting that in eukaryotic Argonaute proteins the RNase H-like domain may possess nuclease activity. The conserved region around the C-terminus of the PIWI domain, which is required for small interfering RNA (siRNA) binding to AfPiwi, may function as the receptor site for the obligatory 5' phosphate of siRNAs, thereby specifying the cleavage position of the target mRNA.
Figures

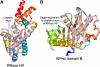

Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanism of target RNA transcript recognition by Argonaute-guide complexes.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:45-50. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.029. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381279 Review.
-
Crystal structure of Argonaute and its implications for RISC slicer activity.Science. 2004 Sep 3;305(5689):1434-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1102514. Epub 2004 Jul 29. Science. 2004. PMID: 15284453
-
Structural insights into mRNA recognition from a PIWI domain-siRNA guide complex.Nature. 2005 Mar 31;434(7033):663-6. doi: 10.1038/nature03462. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15800628 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for 5'-end-specific recognition of guide RNA by the A. fulgidus Piwi protein.Nature. 2005 Mar 31;434(7033):666-70. doi: 10.1038/nature03514. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15800629 Free PMC article.
-
[Components and assembly of RNA-induced silencing complex].Yi Chuan. 2006 Jun;28(6):761-6. Yi Chuan. 2006. PMID: 16818443 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Two novel PIWI families: roles in inter-genomic conflicts in bacteria and Mediator-dependent modulation of transcription in eukaryotes.Biol Direct. 2013 Jun 8;8:13. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-8-13. Biol Direct. 2013. PMID: 23758928 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulations in HIWI level exerts influence on the proliferation of human non-small cell lung cancer cells.Exp Ther Med. 2016 May;11(5):1971-1976. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3106. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27168836 Free PMC article.
-
Computational models with thermodynamic and composition features improve siRNA design.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Feb 12;7:65. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-65. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16472402 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial expression of mouse argonaute 2 for functional and mutational studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2010 Feb 12;11(2):745-53. doi: 10.3390/ijms11020745. Int J Mol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20386665 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the functions of RNA interference pathway proteins: some functions are more RISCy than others?Biochem J. 2005 May 1;387(Pt 3):561-71. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041822. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15845026 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aza-Blanc P, Cooper CL, Wagner K, Batalov S, Deveraux QL, Cooke MP (2003) Identification of modulators of TRAIL-induced apoptosis via RNAi-based phenotypic screening. Mol Cell 12: 627–637 - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297 - PubMed
-
- Barton GJ (1993) ALSCRIPT: a tool to format multiple sequence alignments. Protein Eng 6: 37–40 - PubMed
-
- Baulcombe D (2004) RNA silencing in plants. Nature 431: 356–363 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

