UvrD helicase, unlike Rep helicase, dismantles RecA nucleoprotein filaments in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 15565170
- PMCID: PMC544901
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600485
UvrD helicase, unlike Rep helicase, dismantles RecA nucleoprotein filaments in Escherichia coli
Abstract
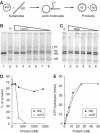
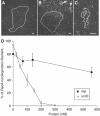
The roles of UvrD and Rep DNA helicases of Escherichia coli are not yet fully understood. In particular, the reason for rep uvrD double mutant lethality remains obscure. We reported earlier that mutations in recF, recO or recR genes suppress the lethality of uvrD rep, and proposed that an essential activity common to UvrD and Rep is either to participate in the removal of toxic recombination intermediates or to favour the proper progression of replication. Here, we show that UvrD, but not Rep, directly prevents homologous recombination in vivo. In addition to RecFOR, we provide evidence that RecA contributes to toxicity in the rep uvrD mutant. In vitro, UvrD dismantles the RecA nucleoprotein filament, while Rep has only a marginal activity. We conclude that UvrD and Rep do not share a common activity that is essential in vivo: while Rep appears to act at the replication stage, UvrD plays a role of RecA nucleoprotein filament remover. This activity of UvrD is similar to that of the yeast Srs2 helicase.
Figures
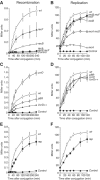
 ), ‘uvrD’ MAC1058 (□), ‘pBR’ MAC1068 (Δ), ‘UvrD++’ MAC1071 (⧫) and ‘rep’ MAC1065 (▪). The ‘control’ curves in panels A, C and E (•) represent the cross between two identical lacZΔP alleles, Nec223 and Nec225 strains, which cannot result in a Lac+ recombinant. The ‘control’ curve in panels B, D and E represents the Hfr3000 lacIs donor strain without any recipient strain (•): it indicates the amount of transcription leakage in the presence of IPTG, with the lacIs allele (around 5 units). After a 40 min conjugation period on filter, β-galactosidase activity of cell extracts was measured as a function of incubation time at 28°C.
), ‘uvrD’ MAC1058 (□), ‘pBR’ MAC1068 (Δ), ‘UvrD++’ MAC1071 (⧫) and ‘rep’ MAC1065 (▪). The ‘control’ curves in panels A, C and E (•) represent the cross between two identical lacZΔP alleles, Nec223 and Nec225 strains, which cannot result in a Lac+ recombinant. The ‘control’ curve in panels B, D and E represents the Hfr3000 lacIs donor strain without any recipient strain (•): it indicates the amount of transcription leakage in the presence of IPTG, with the lacIs allele (around 5 units). After a 40 min conjugation period on filter, β-galactosidase activity of cell extracts was measured as a function of incubation time at 28°C.
References
-
- Arthur HM, Lloyd RG (1980) Hyper-recombination in uvrD mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet 180: 185–191 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

