Active transforming growth factor-beta1 activates the procollagen I promoter in patients with acute lung injury
- PMID: 15565360
- PMCID: PMC7095267
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-004-2503-2
Active transforming growth factor-beta1 activates the procollagen I promoter in patients with acute lung injury
Abstract
Objective: Fibroproliferation markers like procollagen I predict mortality in patients with acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). We sought to determine whether bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from patients with lung injury contained mediators that would activate procollagen I promoter and if this activation predicted important clinical outcomes.
Design: Prospective controlled study of ALI/ARDS.
Setting: Intensive care units and laboratory of a university hospital.
Patients and participants: Acute lung injury/ARDS, cardiogenic edema (negative controls) and pulmonary fibrosis (positive controls) patients.
Interventions: Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid was collected within 48 h of intubation from ALI/ARDS patients. BALF was also collected from patients with pulmonary fibrosis and cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Human lung fibroblasts were transfected with a procollagen I promoter-luciferase construct and incubated with BALF; procollagen I promoter activity was then measured. BALF active TGF-beta1 levels were measured by ELISA.
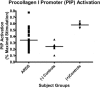
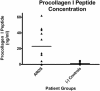
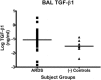
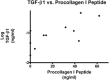
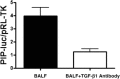
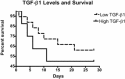
Results: Twenty-nine ARDS patients, nine negative and six positive controls were enrolled. BALF from ARDS patients induced 41% greater procollagen I promoter activation than that from negative controls (p<0.05) and a TGF-beta1 blocking antibody significantly reduced this activation in ARDS patients. There was a trend toward higher TGF-beta1 levels in the ARDS group compared to negative controls (-1.056 log(10)+/-0.1415 vs -1.505 log(10)+/-0.1425) (p<0.09). Procollagen I promoter activation was not associated with mortality; however, lower TGF-beta1 levels were associated with more ventilator-free and ICU-free days.
Conclusions: Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from ALI/ARDS patients activates procollagen I promoter, which is due partly to TGF-beta1. Activated TGF-beta1 may impact ARDS outcome independent of its effect on procollagen I activation.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

