Extravascular lung water assessed by transpulmonary single thermodilution and postmortem gravimetry in sheep
- PMID: 15566591
- PMCID: PMC1065070
- DOI: 10.1186/cc2974
Extravascular lung water assessed by transpulmonary single thermodilution and postmortem gravimetry in sheep
Abstract
Introduction: Acute lung injury is associated with accumulation of extravascular lung water (EVLW). The aim of the present study was to compare two methods for quantification of EVLW: transpulmonary single thermodilution (EVLWST) and postmortem gravimetric (EVLWG).
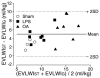
Methods: Eighteen instrumented and awake sheep were randomly assigned to one of three groups. All groups received Ringer's lactate (5 ml/kg per hour intravenously). To induce lung injury of different severities, sheep received Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide 15 ng/kg per min intravenously for 6 hours (n = 7) or oleic acid 0.06 ml/kg intravenously over 30 min (n = 7). A third group (n = 4) was subjected to sham operation. Haemodynamic variables, including EVLWST, were measured using a PiCCOplus monitor (Pulsion Medical Systems, Munich, Germany), and the last measurement of EVLWST was compared with EVLWG.
Results: At the end of experiment, values for EVLWST (mean +/- standard error) were 8.9 +/- 0.6, 11.8 +/- 1.0 and 18.2 +/- 0.9 ml/kg in the sham-operated, lipopolysaccharide and oleic acid groups, respectively (P < 0.05). The corresponding values for EVLWIG were 6.2 +/- 0.3, 7.1 +/- 0.6 and 11.8 +/- 0.7 ml/kg (P < 0.05). Ranges of EVLWIST and EVLWIG values were 7.5-21.0 and 4.9-14.5 ml/kg. Regression analysis between in vivo EVLWST and postmortem EVLWG yielded the following relation: EVLWST = 1.30 x EVLWG + 2.32 (n = 18, r = 0.85, P < 0.0001). The mean bias +/- 2 standard deviations between EVLWST and EVLWG was 4.9 +/- 5.1 ml/kg (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: In sheep, EVLW determined using transpulmonary single thermodilution correlates closely with gravimetric measurements over a wide range of changes. However, transpulmonary single thermodilution overestimates EVLW as compared with postmortem gravimetry.
Figures




References
-
- Martin GS, Bernard GR. Airway and lung in sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2001;27(Suppl 1):S63–S79. - PubMed
-
- Halperin BD, Feeley TW, Mihm FG, Chiles C, Guthaner DF, Blank NE. Evaluation of the portable chest roentgenogram for quantitating extravascular lung water in critically ill adults. Chest. 1985;88:649–652. - PubMed
-
- Pfeiffer UJ, Backus G, Blumel G, Eckart J, Muller P, Winkler P, Zeravik J, Zimmermann GJ. A fiberoptic-based system for integrated monitoring of cardiac output, intrathoracic blood volume, extravascular lung water, O2 saturation, and a-v differences. In: Lewis FR, Pfeiffer UJ, editor. In Practical Applications of Fiberoptics in Critical Care Monitoring. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer; 1990. pp. 114–125.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

