Statistics review 13: receiver operating characteristic curves
- PMID: 15566624
- PMCID: PMC1065080
- DOI: 10.1186/cc3000
Statistics review 13: receiver operating characteristic curves
Abstract
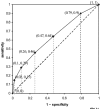
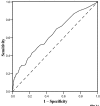
This review introduces some commonly used methods for assessing the performance of a diagnostic test. The sensitivity, specificity and likelihood ratio of a test are discussed. The uses of the receiver operating characteristic curve and the area under the curve are explained.
Figures
References
-
- Petrie A, Sabin C. Medical Statistics at a Glance. Oxford, UK: Blackwell; 2000.
-
- Campbell MJ, Machin D. Medical Statistics: A Commonsense Approach. 3. Chichester, UK: Wiley; 1999.
-
- Hanley JA, McNeil BJ. A method of comparing the areas under receiver operating characteristic curves derived from the same cases. Radiology. 1983;148:839–843. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources