Rheumatoid and psoriatic knee synovitis: clinical, grey scale, and power Doppler ultrasound assessment of the response to etanercept
- PMID: 15567814
- PMCID: PMC1755540
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.025585
Rheumatoid and psoriatic knee synovitis: clinical, grey scale, and power Doppler ultrasound assessment of the response to etanercept
Abstract
Objective: To determine the effect of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) blockade with etanercept in refractory knee joint synovitis (KJS) in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis, by local and systemic disease activity assessment and combined grey scale and power Doppler ultrasonographic monitoring.
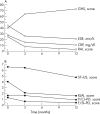
Methods: 27 knees affected by rheumatoid KJS (n = 12) and psoriatic KJS (n = 8) were assessed before receiving treatment and at 3 and 12 months' follow up. Time dependent clinical changes in disease activity were monitored by C reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), global health status (GHS), and Ritchie (RAI) and knee joint articular (KJAI) indices; synovial changes were monitored by ultrasonographic and power Doppler indices for grey scale synovial thickening and for distinct intrasynovial vessel power Doppler flow configurations (fluid/synovium interface (F/SI-PD) and pannus/cartilage interface (P/CI-PD)). Interobserver and intraobserver variability of grey scale and power Doppler ultrasonographic was evaluated. Response to treatment was assessed by analysis of variance for repeated measures on clinical and ultrasonographic variables.
Results: Rapid (3 months) reduction in F/SI-PD flow (p<0.001), parallel to reductions of C reactive protein (p<0.05), ESR (p<0.001), KJAI (p<0.002), RAI, and GHS (p<0.001), was sustained at 12 months when it was accompanied by reduction in both synovial thickening and P/CI-PD flow (p<0.001). No differences (ANOVA) were noted at baseline or at 12 months in clinical and ultrasonographic variables between either the rheumatoid or the psoriatic KJS groups.
Conclusion: Grey scale and power Doppler ultrasonography are reliable measures of long term change in rheumatoid and psoriatic KJS disease activity in response to anti-TNFalpha treatment with etanercept.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation of radiographic progression with the cumulative activity of synovitis estimated by power Doppler ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis: difference between patients treated with methotrexate and those treated with biological agents.J Rheumatol. 2013 Dec;40(12):1967-76. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.130556. Epub 2013 Nov 1. J Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 24187096 Clinical Trial.
-
Calprotectin and TNF trough serum levels identify power Doppler ultrasound synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis patients in remission or with low disease activity.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Jul 8;18(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1032-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27391315 Free PMC article.
-
Power Doppler ultrasonographic monitoring of response to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Aug;58(8):2248-56. doi: 10.1002/art.23682. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18668537 Clinical Trial.
-
Etanercept: an updated review of its use in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.Drugs. 2002;62(17):2493-537. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262170-00013. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12421111 Review.
-
Spotlight on etanercept in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.BioDrugs. 2003;17(2):139-45. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200317020-00006. BioDrugs. 2003. PMID: 12641492 Review.
Cited by
-
Synovial Fluid-Derived Extracellular Vesicles of Patients with Arthritides Contribute to Hippocampal Synaptic Dysfunctions and Increase with Mood Disorders Severity in Humans.Cells. 2022 Jul 23;11(15):2276. doi: 10.3390/cells11152276. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35892573 Free PMC article.
-
Knee joint synovitis: study of correlations and diagnostic performances of ultrasonography compared with histopathology.RMD Open. 2018 Feb 8;4(1):e000616. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000616. eCollection 2018. RMD Open. 2018. PMID: 29531789 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound assessment of enthesis thickening in psoriatic arthritis patients treated with adalimumab compared to methotrexate.Clin Rheumatol. 2016 Feb;35(2):363-70. doi: 10.1007/s10067-014-2753-5. Epub 2014 Jul 31. Clin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 25073614
-
[Ultrasound and arthritis].Z Rheumatol. 2010 Dec;69(10):889-901; quiz 902. doi: 10.1007/s00393-010-0730-1. Z Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 21128050 Review. German.
-
The role of ultrasonography in monitoring long-standing rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot study.Reumatologia. 2017;55(4):177-182. doi: 10.5114/reum.2017.69781. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Reumatologia. 2017. PMID: 29056772 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

