Tumor progression while on chemotherapy: a contraindication to liver resection for multiple colorectal metastases?
- PMID: 15570210
- PMCID: PMC1356520
- DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000145964.08365.01
Tumor progression while on chemotherapy: a contraindication to liver resection for multiple colorectal metastases?
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the influence of the response to preoperative chemotherapy, especially tumor progression, on the outcome following resection of multiple colorectal liver metastases (CRM).
Summary background data: Hepatic resection is the only treatment that currently offers a chance of long-term survival, although it is associated with a poor outcome in patients with multinodular CRM. Because of its better efficacy, chemotherapy is increasingly proposed as neoadjuvant treatment in such patients to allow or to facilitate the radicality of resection. However, little is known of the efficacy of such a strategy and the influence of the response to chemotherapy on the outcome of hepatic resection.
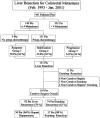
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the course of 131 consecutive patients who underwent liver resection for multiple (> or =4) CRM after systemic chemotherapy between 1993 and 2000, representing 30% of all liver resections performed for CRM in our institution during that period. Chemotherapy included mainly 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and either oxaliplatin or irinotecan for a mean of 9.8 courses (median, 9 courses). Patients were divided into 3 groups according to the type of response obtained to preoperative chemotherapy. All liver resections were performed with curative intent. We analyzed patient outcome in relation to response to preoperative chemotherapy.
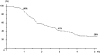
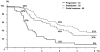
Results: There were 58 patients (44%) who underwent hepatectomy after an objective tumor response (group 1), 39 (30%) after tumor stabilization (group 2), and 34 (26%) after tumor progression (group 3). At the time of diagnosis, mean tumor size and number of metastases were similar in the 3 groups. No differences were observed regarding patient demographics, characteristics of the primary tumor, type of liver resection, and postoperative course. First line treatments were different between groups with a higher proportion of oxaliplatin- and/or irinotecan-based treatments in group 1 (P < 0.01). A higher number of lines of chemotherapy were used in group 2 (P = 0.002). Overall survival was 86%, 41%, and 28% at 1, 3, and 5 years, respectively. Five-year survival was much lower in group 3 compared with groups 1 and 2 (8% vs. 37% and 30%, respectively at 5 years, P < 0.0001). Disease-free survival was 3% compared with 21% and 20%, respectively (P = 0.02). In a multivariate analysis, tumor progression on chemotherapy (P < 0.0001), elevated preoperative serum CA 19-9 (P < 0.0001), number of resected metastases (P < 0.001), and the number of lines of chemotherapy (P < 0.04), but not the type of first line treatment, were independently associated with decreased survival.
Conclusions: Liver resection is able to offer long-term survival to patients with multiple colorectal metastases provided that the metastatic disease is controlled by chemotherapy prior to surgery. Tumor progression before surgery is associated with a poor outcome, even after potentially curative hepatectomy. Tumor control before surgery is crucial to offer a chance of prolonged remission in patients with multiple metastases.
Figures

References
-
- Stangl R, Altendorf-Hofmann A, Charnley RM, et al. Factors influencing the natural history of colorectal liver metastases. Lancet. 1994;343:1405–1410. - PubMed
-
- Nordlinger B, Guiguet M, Vaillant JC, et al. Surgical resection of colorectal carcinoma metastases to the liver: a prognostic scoring system to improve case selection based on 1588 patients. Assoc Fr Chirurgie Cancer. 1996;77:1254–1262. - PubMed
-
- Scheele J, Strangl R, Altendorf-Hofmann A, et al. Resection of colorectal liver metastases. World J Surg. 1995;19:59–71. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

