Restoration of NF-kappaB activation by tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor complex-targeted MEKK3 in receptor-interacting protein-deficient cells
- PMID: 15572679
- PMCID: PMC533972
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.24.10757-10765.2004
Restoration of NF-kappaB activation by tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor complex-targeted MEKK3 in receptor-interacting protein-deficient cells
Abstract
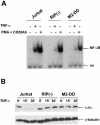
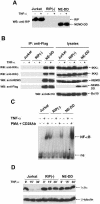
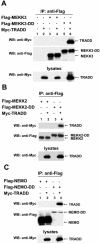
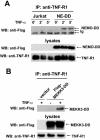
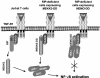
Receptor-interacting protein (RIP) plays a critical role in tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)-induced NF-kappaB activation. However, the mechanism by which RIP mediates TNF-alpha-induced signal transduction is not fully understood. In this study, we reconstituted RIP-deficient Jurkat T cells with a fusion protein composed of full-length MEKK3 and the death domain of RIP (MEKK3-DD). In these cells, MEKK3-DD substitutes for RIP and directly associates with TRADD in TNF receptor complexes following TNF-alpha stimulation. We found that TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation was fully restored by MEKK3-DD in these cells. In contrast, expression of a fusion protein composed of NEMO, a component of the IkappaB kinase complex, and the death domain of RIP (NEMO-DD) cannot restore TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation in RIP-deficient cells. These results indicate that the role of RIP is to specifically recruit MEKK3 to the TNF-alpha receptor complex, whereas the forced recruitment of NEMO to the TNF-alpha receptor complex is insufficient for TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation. Although MEKK2 has a high degree of homology with MEKK3, MEKK2-DD, unlike MEKK3-DD, also fails to restore TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation in RIP-deficient cells, indicating that RIP-dependent recruitment of MEKK3 plays a specific role in TNF-alpha signaling.
Figures





References
-
- Blank, J. L., P. Gerwins, E. M. Elliott, S. Sather, and G. L. Johnson. 1996. Molecular cloning of mitogen-activated protein/ERK kinase kinases (MEKK) 2 and 3. Regulation of sequential phosphorylation pathways involving mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 271:5361-5368. - PubMed
-
- Bouwmeester, T., A. Bauch, H. Ruffner, P. O. Angrand, G. Bergamini, K. Croughton, C. Cruciat, D. Eberhard, J. Gagneur, S. Ghidelli, C. Hopf, B. Huhse, R. Mangano, A. M. Michon, M. Schirle, J. Schlegl, M. Schwab, M. A. Stein, A. Bauer, G. Casari, G. Drewes, A. C. Gavin, D. B. Jackson, G. Joberty, G. Neubauer, J. Rick, B. Kuster, and G. Superti-Furga. 2004. A physical and functional map of the human TNF-alpha/NF-kappa B signal transduction pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 6:97-105. - PubMed
-
- Chen, G., and D. V. Goeddel. 2002. TNF-R1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science 296:1634-1635. - PubMed
-
- Devin, A., A. Cook, Y. Lin, Y. Rodriguez, M. Kelliher, and Z. Liu. 2000. The distinct roles of TRAF2 and RIP in IKK activation by TNF-R1: TRAF2 recruits IKK to TNF-R1 while RIP mediates IKK activation. Immunity 12:419-429. - PubMed
-
- Ellinger-Ziegelbauer, H., K. Brown, K. Kelly, and U. Siebenlist. 1997. Direct activation of the stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) pathways by an inducible mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase kinase 3 (MEKK) derivative. J. Biol. Chem. 272:2668-2674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
