The AMP-activated protein kinase AAK-2 links energy levels and insulin-like signals to lifespan in C. elegans
- PMID: 15574588
- PMCID: PMC535911
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1255404
The AMP-activated protein kinase AAK-2 links energy levels and insulin-like signals to lifespan in C. elegans
Erratum in
- Genes Dev. 2005 Feb 1;19(3):411
- Genes Dev. 2005 Jan 1;19(1):188
Abstract
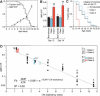
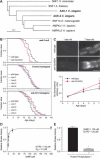
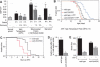
Although limiting energy availability extends lifespan in many organisms, it is not understood how lifespan is coupled to energy levels. We find that the AMP:ATP ratio, a measure of energy levels, increases with age in Caenorhabditis elegans and can be used to predict life expectancy. The C. elegans AMP-activated protein kinase alpha subunit AAK-2 is activated by AMP and functions to extend lifespan. In addition, either an environmental stressor that increases the AMP:ATP ratio or mutations that lower insulin-like signaling extend lifespan in an aak-2-dependent manner. Thus, AAK-2 is a sensor that couples lifespan to information about energy levels and insulin-like signals.
Figures

References
-
- Andersson U., Filipsson, K., Abbott, C.R., Woods, A., Smith, K., Bloom, S.R., Carling, D., and Small, C.J. 2004. AMP-activated protein kinase plays a role in the control of food intake. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 12005-12008. - PubMed
-
- Apfeld J. and Kenyon, C. 1999. Regulation of lifespan by sensory perception in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 402: 804-809. - PubMed
-
- Beauloye C., Marsin, A.S., Bertrand, L., Krause, U., Hardie, D.G., Vanoverschelde, J.L., and Hue, L. 2001. Insulin antagonizes AMP-activated protein kinase activation by ischemia or anoxia in rat hearts, without affecting total adenine nucleotides. FEBS Lett. 505: 348-352. - PubMed
-
- Cypser J.R. and Johnson, T.E. 2002. Multiple stressors in Caenorhabditis elegans induce stress hormesis and extended longevity. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 57: B109-B114. - PubMed
-
- Davies S.P., Carling, D., and Hardie, D.G. 1989. Tissue distribution of the AMP-activated protein kinase, and lack of activation by cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase, studied using a specific and sensitive peptide assay. Eur. J. Biochem. 186: 123-128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
