The Drosha-DGCR8 complex in primary microRNA processing
- PMID: 15574589
- PMCID: PMC535913
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1262504
The Drosha-DGCR8 complex in primary microRNA processing
Abstract
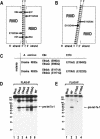
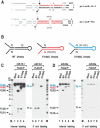
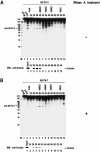
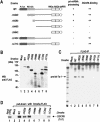
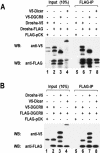
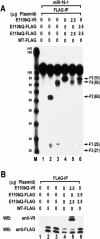
RNase III proteins play key roles in microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis. The nuclear RNase III Drosha cleaves primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs) to release hairpin-shaped pre-miRNAs that are subsequently cut by the cytoplasmic RNase III Dicer to generate mature miRNAs. While Dicer (class III) and other simple RNase III proteins (class I) have been studied intensively, the class II enzyme Drosha remains to be characterized. Here we dissected the action mechanism of human Drosha by generating mutants and by characterizing its new interacting partner, DGCR8. The basic action mechanism of Drosha was found to be similar to that of human Dicer; the RNase III domains A and B form an intramolecular dimer and cleave the 3' and 5' strands of the stem, respectively. Human Drosha fractionates at approximately 650 kDa, indicating that Drosha functions as a large complex. In this complex, Drosha interacts with DGCR8, which contains two double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-binding domains. By RNAi and biochemical reconstitution, we show that DGCR8 may be an essential component of the pri-miRNA processing complex, along with Drosha. Based on these results, we propose a model for the action mechanism of class II RNase III proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Bartel D.P. 2004. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281-297. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E., Caudy, A.A., Hammond, S.M., and Hannon, G.J. 2001. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409: 363-366. - PubMed
-
- Blaszczyk J., Tropea, J.E., Bubunenko, M., Routzahn, K.M., Waugh, D.S., Court, D.L., and Ji, X. 2001. Crystallographic and modeling studies of RNase III suggest a mechanism for double-stranded RNA cleavage. Structure (Camb) 9: 1225-1236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
