Contribution of Asian mouse subspecies Mus musculus molossinus to genomic constitution of strain C57BL/6J, as defined by BAC-end sequence-SNP analysis
- PMID: 15574823
- PMCID: PMC534668
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.2899304
Contribution of Asian mouse subspecies Mus musculus molossinus to genomic constitution of strain C57BL/6J, as defined by BAC-end sequence-SNP analysis
Abstract
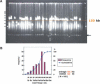
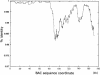
MSM/Ms is an inbred strain derived from the Japanese wild mouse, Mus musculus molossinus. It is believed that subspecies molossinus has contributed substantially to the genome constitution of common laboratory strains of mice, although the majority of their genome is derived from the west European M. m. domesticus. Information on the molossinus genome is thus essential not only for genetic studies involving molossinus but also for characterization of common laboratory strains. Here, we report the construction of an arrayed bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library from male MSM/Ms genomic DNA, covering approximately 1x genome equivalent. Both ends of 176,256 BAC clone inserts were sequenced, and 62,988 BAC-end sequence (BES) pairs were mapped onto the C57BL/6J genome (NCBI mouse Build 30), covering 2,228,164 kbp or 89% of the total genome. Taking advantage of the BES map data, we established a computer-based clone screening system. Comparison of the MSM/Ms and C57BL/6J sequences revealed 489,200 candidate single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 51,137,941 bp sequenced. The overall nucleotide substitution rate was as high as 0.0096. The distribution of SNPs along the C57BL/6J genome was not uniform: The majority of the genome showed a high SNP rate, and only 5.2% of the genome showed an extremely low SNP rate (percentage identity = 0.9997); these sequences are likely derived from the molossinus genome.
Figures

References
-
- Atchley, W.R. and Fitch, W.M. 1991. Gene trees and the origins of inbred strains of mice. Science 254: 554-558. - PubMed
-
- Beck, J.A, Lloyd, S., Hafezparast, M., Lennon-Pierce, M., Eppig, J.T., Festing, M.F., and Fisher, E.M. 2000. Genealogies of mouse inbred strains. Nat. Genet. 24: 23-25. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, C.E., Boursot, P., Baron, B., Bonhomme, F., and Hatat, D. 1985. Most classical Mus musculus domesticus laboratory mouse strains carry a Mus musculus musculus Y chromosome. Nature 315: 70-72. - PubMed
-
- Bonhomme, F., Guenet J.-L., Dod, B., Moriwaki, K., and Bulfield, G. 1987. The polyphyletic origin of laboratory inbred mice and their rate of evolution. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. 30: 51-58.
Web site references
-
- http://www.shigen.nig.ac.jp/mouse/mmdbj/top.jsp; Mouse Microsatellite Database of Japan.
-
- http://stt.gsc.riken.jp/msm/; Web browser-based BAC library screening system.
-
- http://shigen.lab.nig.ac.jp/mouse/polymorphism/; a browser-based clone screening system site.
-
- http://analysis1.lab.nig.ac.jp/Mus_musculus/; the MSM BAC database, and a browser-based clone screening system site.
-
- http://www.brc.riken.jp/lab/dna/; the RIKEN BioResource Center DNA bank.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
