ADAM12 and alpha9beta1 integrin are instrumental in human myogenic cell differentiation
- PMID: 15574885
- PMCID: PMC545917
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-03-0226
ADAM12 and alpha9beta1 integrin are instrumental in human myogenic cell differentiation
Abstract
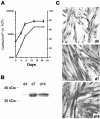
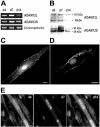
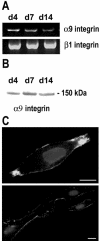
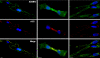
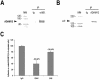
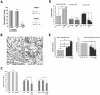
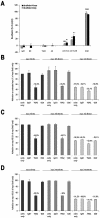
Knowledge on molecular systems involved in myogenic precursor cell (mpc) fusion into myotubes is fragmentary. Previous studies have implicated the a disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) family in most mammalian cell fusion processes. ADAM12 is likely involved in fusion of murine mpc and human rhabdomyosarcoma cells, but it requires yet unknown molecular partners to launch myogenic cell fusion. ADAM12 was shown able to mediate cell-to-cell attachment through binding alpha9beta1 integrin. We report that normal human mpc express both ADAM12 and alpha9beta1 integrin during their differentiation. Expression of alpha9 parallels that of ADAM12 and culminates at time of fusion. alpha9 and ADAM12 coimmunoprecipitate and participate to mpc adhesion. Inhibition of ADAM12/alpha9beta1 integrin interplay, by either ADAM12 antisense oligonucleotides or blocking antibody to alpha9beta1, inhibited overall mpc fusion by 47-48%, with combination of both strategies increasing inhibition up to 62%. By contrast with blockade of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1/alpha4beta1, which also reduced fusion, exposure to ADAM12 antisense oligonucleotides or anti-alpha9beta1 antibody did not induce detachment of mpc from extracellular matrix, suggesting specific involvement of ADAM12-alpha9beta1 interaction in the fusion process. Evaluation of the fusion rate with regard to the size of myotubes showed that both ADAM12 antisense oligonucleotides and alpha9beta1 blockade inhibited more importantly formation of large (> or =5 nuclei) myotubes than that of small (2-4 nuclei) myotubes. We conclude that both ADAM12 and alpha9beta1 integrin are expressed during postnatal human myogenic differentiation and that their interaction is mainly operative in nascent myotube growth.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hierarchy of ADAM12 binding to integrins in tumor cells.Exp Cell Res. 2005 Oct 1;309(2):438-50. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.06.020. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 16061220
-
Interaction of the disintegrin and cysteine-rich domains of ADAM12 with integrin alpha7beta1.Exp Cell Res. 2004 Aug 1;298(1):28-37. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.04.005. Exp Cell Res. 2004. PMID: 15242759
-
RGD-independent binding of integrin alpha9beta1 to the ADAM-12 and -15 disintegrin domains mediates cell-cell interaction.J Biol Chem. 2000 Nov 10;275(45):34922-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M001953200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10944520
-
The newcomer in the integrin family: integrin α9 in biology and cancer.Adv Biol Regul. 2012 May;52(2):326-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2012.03.004. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Adv Biol Regul. 2012. PMID: 22781746 Review.
-
The ADAM-integrin-tetraspanin complex in fetal and postnatal testicular cords.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2005 Jun;75(2):130-41. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.20041. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2005. PMID: 16035044 Review.
Cited by
-
The regulatory role of Myomaker and Myomixer-Myomerger-Minion in muscle development and regeneration.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Apr;77(8):1551-1569. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03341-9. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31642939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ADAM12-directed ectodomain shedding of E-cadherin potentiates trophoblast fusion.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Dec;22(12):1970-84. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.44. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25909890 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the role of integrins and integrins-targeting biomaterials in bone regeneration.Connect Tissue Res. 2024 Sep;65(5):343-363. doi: 10.1080/03008207.2024.2396002. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Connect Tissue Res. 2024. PMID: 39297793 Review.
-
Transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) is an inhibitory factor for adult myogenesis.Skelet Muscle. 2021 May 29;11(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13395-021-00271-8. Skelet Muscle. 2021. PMID: 34051858 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin expression in coculture of differentiating rat fetal skeletal fibroblasts and myoblasts.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2006 Jan-Feb;42(1-2):4-7. doi: 10.1007/s11626-006-0003-0. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2006. PMID: 16618210
References
-
- Abe, E., Mocharla, H., Yamate, T., Taguchi, Y., and Manolagas, S. C. (1999). Meltrin-alpha, a fusion protein involved in multinucleated giant cell and osteoclast formation. Calcif. Tissue Int. 64, 508-515. - PubMed
-
- Abmayr, S. M., Balagopalan, L., Galletta, B. J., and Hong, S. J. (2003). Cell and molecular biology of myoblast fusion. Int. Rev. Cytol. 225, 33-89. - PubMed
-
- Asakura, M., et al. (2002). Cardiac hypertrophy is inhibited by antagonism of ADAM12 processing of HB-epidermal growth factor: metalloproteinase inhibitors as a new therapy. Nat. Med. 8, 35-40. - PubMed
-
- Authier, F. J., Chazaud, B., Plonquet, A., Eliezer-Vanerot, M. C., Poron, F., Belec, L., Barlovatz-Meimon, G., and Gherardi, R. K. (1999). Differential expression of the IL-1 system components during in vitro myogenesis: implication of IL-1beta in induction of myogenic cell apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6, 1012-1021. - PubMed
-
- Barnoy, S., Glasner, T., and Kosower, N. S. (1996). The role of calpastatin (the specific calpain inhibitor) in myoblast differentiation and fusion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 220, 933-938. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

