Nucleotide sequences, genetic organization, and distribution of pEU30 and pEL60 from Erwinia amylovora
- PMID: 15574957
- PMCID: PMC535195
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.12.7539-7544.2004
Nucleotide sequences, genetic organization, and distribution of pEU30 and pEL60 from Erwinia amylovora
Abstract
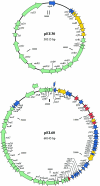
The nucleotide sequences, genetic organization, and distribution of plasmids pEU30 (30,314 bp) and pEL60 (60,145 bp) from the plant pathogen Erwinia amylovora are described. The newly characterized pEU30 and pEL60 plasmids inhabited strains isolated in the western United States and Lebanon, respectively. The gene content of pEU30 resembled plasmids found in plant-associated bacteria, while that of pEL60 was most similar to IncL/M plasmids inhabiting enteric bacteria.
Figures

References
-
- Chiou, C.-S., and A. L. Jones. 1991. The analysis of plasmid-mediated streptomycin resistance in Erwinia amylovora. Phytopathology 81:710-714.
-
- Falkenstein, H., W. Zeller, and K. Geider. 1989. The 29 kb plasmid common in strains of Erwinia amylovora modulates development of fire blight symptoms. J. Gen. Microbiol. 135:2643-2650.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

