Characterisation of cytotoxicity and DNA damage induced by the topoisomerase II-directed bisdioxopiperazine anti-cancer agent ICRF-187 (dexrazoxane) in yeast and mammalian cells
- PMID: 15575955
- PMCID: PMC545072
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2210-4-31
Characterisation of cytotoxicity and DNA damage induced by the topoisomerase II-directed bisdioxopiperazine anti-cancer agent ICRF-187 (dexrazoxane) in yeast and mammalian cells
Abstract
Background: Bisdioxopiperazine anti-cancer agents are inhibitors of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase II, sequestering this protein as a non-covalent protein clamp on DNA. It has been suggested that such complexes on DNA represents a novel form of DNA damage to cells. In this report, we characterise the cytotoxicity and DNA damage induced by the bisdioxopiperazine ICRF-187 by a combination of genetic and molecular approaches. In addition, the well-established topoisomerase II poison m-AMSA is used for comparison.
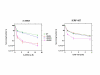
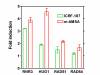
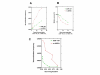
Results: By utilizing a panel of Saccharomyces cerevisiae single-gene deletion strains, homologous recombination was identified as the most important DNA repair pathway determining the sensitivity towards ICRF-187. However, sensitivity towards m-AMSA depended much more on this pathway. In contrast, disrupting the post replication repair pathway only affected sensitivity towards m-AMSA. Homologous recombination (HR) defective irs1SF chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells showed increased sensitivity towards ICRF-187, while their sensitivity towards m-AMSA was increased even more. Furthermore, complementation of the XRCC3 deficiency in irs1SF cells fully abrogated hypersensitivity towards both drugs. DNA-PKcs deficient V3-3 CHO cells having reduced levels of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) showed slightly increased sensitivity to both drugs. While exposure of human small cell lung cancer (SCLC) OC-NYH cells to m-AMSA strongly induced gammaH2AX, exposure to ICRF-187 resulted in much less induction, showing that ICRF-187 generates fewer DNA double strand breaks than m-AMSA. Accordingly, when yeast cells were exposed to equitoxic concentrations of ICRF-187 and m-AMSA, the expression of DNA damage-inducible genes showed higher levels of induction after exposure to m-AMSA as compared to ICRF-187. Most importantly, ICRF-187 stimulated homologous recombination in SPD8 hamster lung fibroblast cells to lower levels than m-AMSA at all cytotoxicity levels tested, showing that the mechanism of action of bisdioxopiperazines differs from that of classical topoisomerase II poisons in mammalian cells.
Conclusion: Our results point to important differences in the mechanism of cytotoxicity induced by bisdioxopiperazines and topoisomerase II poisons, and suggest that bisdioxopiperazines kill cells by a combination of DNA break-related and DNA break-unrelated mechanisms.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human small cell lung cancer NYH cells selected for resistance to the bisdioxopiperazine topoisomerase II catalytic inhibitor ICRF-187 demonstrate a functional R162Q mutation in the Walker A consensus ATP binding domain of the alpha isoform.Cancer Res. 1999 Jul 15;59(14):3442-50. Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10416608
-
Chinese hamster ovary cells resistant to the topoisomerase II catalytic inhibitor ICRF-159: a Tyr49Phe mutation confers high-level resistance to bisdioxopiperazines.Cancer Res. 1998 Apr 1;58(7):1460-8. Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9537249
-
DNA topoisomerase II is the molecular target of bisdioxopiperazine derivatives ICRF-159 and ICRF-193 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Cancer Res. 1995 Jun 1;55(11):2299-303. Cancer Res. 1995. PMID: 7757979
-
Ionizing radiation and genetic risks XIV. Potential research directions in the post-genome era based on knowledge of repair of radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in mammalian somatic cells and the origin of deletions associated with human genomic disorders.Mutat Res. 2005 Oct 15;578(1-2):333-70. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.06.020. Epub 2005 Aug 5. Mutat Res. 2005. PMID: 16084534 Review.
-
Type II topoisomerases--inhibitors, repair mechanisms and mutations.Mutagenesis. 2009 Nov;24(6):465-9. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gep035. Epub 2009 Sep 17. Mutagenesis. 2009. PMID: 19762349 Review.
Cited by
-
Dexrazoxane prevents doxorubicin-induced long-term cardiotoxicity and protects myocardial mitochondria from genetic and functional lesions in rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Jul;151(6):771-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707294. Epub 2007 May 21. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17519947 Free PMC article.
-
Topoisomerase II-mediated DNA damage is differently repaired during the cell cycle by non-homologous end joining and homologous recombination.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 2;5(9):e12541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012541. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20824055 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Damage-Response Pathway Heterogeneity of Human Lung Cancer A549 and H1299 Cells Determines Sensitivity to 8-Chloro-Adenosine.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 28;19(6):1587. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061587. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29843366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andoh T, Ishida R. Catalytic inhibitors of DNA topoisomerase II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1400:155–171. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

