Complete set of orthogonal 21st aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-amber, ochre and opal suppressor tRNA pairs: concomitant suppression of three different termination codons in an mRNA in mammalian cells
- PMID: 15576346
- PMCID: PMC535668
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh959
Complete set of orthogonal 21st aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-amber, ochre and opal suppressor tRNA pairs: concomitant suppression of three different termination codons in an mRNA in mammalian cells
Abstract
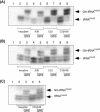
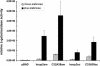
We describe the generation of a complete set of orthogonal 21st synthetase-amber, ochre and opal suppressor tRNA pairs including the first report of a 21st synthetase-ochre suppressor tRNA pair. We show that amber, ochre and opal suppressor tRNAs, derived from Escherichia coli glutamine tRNA, suppress UAG, UAA and UGA termination codons, respectively, in a reporter mRNA in mammalian cells. Activity of each suppressor tRNA is dependent upon the expression of E.coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase, indicating that none of the suppressor tRNAs are aminoacylated by any of the twenty aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in the mammalian cytoplasm. Amber, ochre and opal suppressor tRNAs with a wide range of activities in suppression (increases of up to 36, 156 and 200-fold, respectively) have been generated by introducing further mutations into the suppressor tRNA genes. The most active suppressor tRNAs have been used in combination to concomitantly suppress two or three termination codons in an mRNA. We discuss the potential use of these 21st synthetase-suppressor tRNA pairs for the site-specific incorporation of two or, possibly, even three different unnatural amino acids into proteins and for the regulated suppression of amber, ochre and opal termination codons in mammalian cells.
Figures
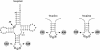



References
-
- Köhrer C. and RajBhandary,U.L. (2004) Proteins carrying one or more unnatural amino acids. In Ibba,M., Francklyn,C. and Cusack,S. (eds), Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases. Landes Bioscience, Georgetown, TX.
-
- Wang L., Brock,A., Herberich,B. and Schultz,P.G. (2001) Expanding the genetic code of Escherichia coli. Science, 292, 498–500. - PubMed
-
- Sakamoto K., Hayashi,A., Sakamoto,A., Kiga,D., Nakayama,H., Soma,A., Kobayashi,T., Kitabatake,M., Takio,K., Saito,K., Shirouzu,M., Hirao,I. and Yokoyama,S. (2002) Site-specific incorporation of an unnatural amino acid into proteins in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res., 30, 4692–4699. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chin J.W., Cropp,T.A., Anderson,J.C., Mukherji,M., Zhang,Z. and Schultz,P.G. (2003) An expanded eukaryotic genetic code. Science, 301, 964–967. - PubMed
-
- Nowak M.W., Kearney,P.C., Sampson,J.R., Saks,M.E., Labarca,C.G., Silverman,S.K., Zhong,W., Thorson,J., Abelson,J.N., Davidson,N. et al. (1995) Nicotinic receptor binding site probed with unnatural amino acid incorporation in intact cells. Science, 268, 439–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

