Hippocampal sharp wave bursts coincide with neocortical "up-state" transitions
- PMID: 15576887
- PMCID: PMC534698
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.73504
Hippocampal sharp wave bursts coincide with neocortical "up-state" transitions
Abstract
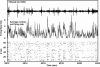
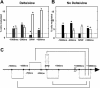
The sleeping neocortex shows nested oscillatory activity in different frequency ranges, characterized by fluctuations between "up-states" and "down-states." High-density neuronal ensemble recordings in rats now reveal the interaction between synchronized activity in the hippocampus and neocortex: Electroencephalographic sharp waves in the hippocampus were more probable during down-states than during up-states, and tended to coincide with transitions from down-states to up-states. The form of cortical activity fluctuations and their interactions with sharp waves depend on sleep depth: In deeper sleep stages, characterized by strong neocortical oscillation in the delta range or slower (approximately 0.8-4 Hz), sharp-wave-triggered peri-event time histograms (PETH) are consistent with a longer duration for down-states than for up-states. In lighter sleep, the sharp-wave-triggered PETH suggested longer up-states than down-states. These results highlight the interplay in the hippocampal/neocortical loop: Decreased neocortical input during down-states may be a factor in generation of sharp waves. In turn, sharp waves may facilitate down-to-up transitions. This interplay may reflect joint memory trace reactivation in the hippocampus and in the neocortex, possibly contributing to consolidation of long-term memory: Off-line reactivation of recent neural activity patterns in the hippocampus occurs during 50-100-msec electroencephalographic sharp waves, corresponding to pyramidal-cell population bursts. The neocortical up-states starting in correspondence with sharp waves may be influenced by the reactivated information carried by the hippocampal sharp wave.
Figures



References
-
- Achermann, P. and Borbely, A.A. 1997. Low-frequency (<1 Hz) oscillations in the human sleep electroencephalogram. Neuroscience 81: 213-222. - PubMed
-
- Ball, G.J., Gloor, P., and Schaul, N. 1977. The cortical electromicrophysiology of pathological delta waves in the electroencephalogram of cats. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 43: 346-361. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia, F.P, Sutherland, G.R., and McNaughton, B.L. 2001. Widespread modulation of neocortical cell activity during hippocampal sharp waves. Soc. Neurosci. Abs. 27: 643.16.
-
- Buzsaki, G. 1989. Two-stage model of memory trace formation: A role for “noisy” brain states. Neuroscience 31: 551-570. - PubMed
-
- Buzsaki, G., Horvath, Z., Urioste, R., Hetke, J., and Wise, K. 1992. High-frequency network oscillation in the hippocampus. Science 256: 1025-1027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
