Always look on the bright site of Rho: structural implications for a conserved intermolecular interface
- PMID: 15577926
- PMCID: PMC1299188
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400293
Always look on the bright site of Rho: structural implications for a conserved intermolecular interface
Abstract
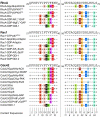
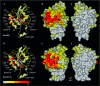
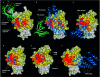
The signalling functions of Rho-family GTPases are based on the formation of distinctive protein-protein complexes. Invaluable insights into the structure-function relationships of the Rho GTPases have been obtained through the resolution of several of their structures in complex with regulators and downstream effectors. In this review, we use these complexes to compare the binding and specificity-determining sites of the Rho GTPases. Although the properties that characterize these sites are diverse, some fundamental conserved principles that govern their intermolecular interactions have emerged. Notably, all of the interacting partners of the Rho GTPases, irrespective of their function, bind to a common set of conserved amino acids that are clustered on the surface of the switch regions. This conserved region and its specific structural characteristics exemplify the convergence of the Rho GTPases on a consensus binding site.
Figures



References
-
- Abdul-Manan N et al. (1999) Structure of Cdc42 in complex with the GTPase-binding domain of the 'Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome' protein. Nature 399: 379–383 - PubMed
-
- Ahmadian MR, Stege P, Scheffzek K, Wittinghofer A (1997) Confirmation of the arginine-finger hypothesis for the GAPstimulated GTP-hydrolysis reaction of Ras. Nat Struct Biol 4: 686–689 - PubMed
-
- Blumenstein L, Ahmadian MR (2004) Models of the cooperative mechanism for Rho-effector recognition: implications for RhoA-mediated effector activation. J Biol Chem Oct 8 [epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Boquet P, Lemichez E (2003) Bacterial virulence factors targeting Rho GTPases: parasitism or symbiosis? Trends Cell Biol 13: 238–246 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

