Regulation of eukaryotic translation by the RACK1 protein: a platform for signalling molecules on the ribosome
- PMID: 15577927
- PMCID: PMC1299186
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400291
Regulation of eukaryotic translation by the RACK1 protein: a platform for signalling molecules on the ribosome
Abstract
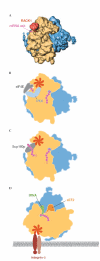
The receptor for activated C-kinase (RACK1) is a scaffold protein that is able to interact simultaneously with several signalling molecules. It binds to protein kinases and membrane-bound receptors in a regulated fashion. Interestingly, RACK1 is also a constituent of the eukaryotic ribosome, and a recent cryo-electron microscopy study localized it to the head region of the 40S subunit in the vicinity of the messenger RNA (mRNA) exit channel. RACK1 recruits activated protein kinase C to the ribosome, which leads to the stimulation of translation through the phosphorylation of initiation factor 6 and, potentially, of mRNA-associated proteins. RACK1 therefore links signal-transduction pathways directly to the ribosome, which allows translation to be regulated in response to cell stimuli. In addition, the fact that RACK1 associates with membrane-bound receptors indicates that it promotes the docking of ribosomes at sites where local translation is required, such as focal adhesions.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Communication between RACK1/Asc1 and uS3 (Rps3) is essential for RACK1/Asc1 function in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Gene. 2019 Jul 20;706:69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.04.087. Epub 2019 May 1. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31054365 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the versatile scaffold protein RACK1 on the eukaryotic ribosome by cryo-EM.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004 Oct;11(10):957-62. doi: 10.1038/nsmb822. Epub 2004 Aug 29. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15334071
-
Involvement of Arabidopsis RACK1 in protein translation and its regulation by abscisic acid.Plant Physiol. 2011 Jan;155(1):370-83. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.160663. Epub 2010 Nov 19. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21098678 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analysis of ribosomal RACK1 and its role in translational control.Cell Signal. 2017 Jul;35:272-281. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.01.026. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Cell Signal. 2017. PMID: 28161490 Review.
-
RACK1 research - ships passing in the night?FEBS Lett. 2012 Aug 14;586(17):2787-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.04.048. Epub 2012 May 8. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22580388 Review.
Cited by
-
Crystal structure of Gib2, a signal-transducing protein scaffold associated with ribosomes in Cryptococcus neoformans.Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 3;5:8688. doi: 10.1038/srep08688. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25732347 Free PMC article.
-
TOR and S6K1 promote translation reinitiation of uORF-containing mRNAs via phosphorylation of eIF3h.EMBO J. 2013 Apr 17;32(8):1087-102. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.61. Epub 2013 Mar 22. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23524850 Free PMC article.
-
The Not4 RING E3 Ligase: A Relevant Player in Cotranslational Quality Control.ISRN Mol Biol. 2013 Jan 21;2013:548359. doi: 10.1155/2013/548359. eCollection 2013. ISRN Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 27335678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RACK1 is evolutionary conserved in satellite stem cell activation and adult skeletal muscle regeneration.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Nov 18;8(1):459. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01250-8. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 36396939 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting RACK1 to alleviate TDP-43 and FUS proteinopathy-mediated suppression of protein translation and neurodegeneration.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Dec 18;11(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01705-8. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023. PMID: 38111057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Besson A, Wilson TL, Yong VW (2002) The anchoring protein RACK1 links protein kinase Cε to integrin-β chains. Requirements for adhesion and motility. J Biol Chem 277: 22073–22084 - PubMed
-
- Buensuceso CS, Woodside D, Huff JL, Plopper GE, O'Toole TE (2001) The WD protein Rack1 mediates protein kinase C and integrin-dependent cell migration. J Cell Sci 114: 1691–1698 - PubMed
-
- Ceci M, Gaviraghi C, Gorrini C, Sala LA, Offenhauser N, Marchisio PC, Biffo S (2003) Release of eIF6 (p27BBP) from the 60S subunit allows 80S ribosome assembly. Nature 426: 579–584 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

