Molecular basis for TPR domain-mediated regulation of protein phosphatase 5
- PMID: 15577939
- PMCID: PMC544909
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600496
Molecular basis for TPR domain-mediated regulation of protein phosphatase 5
Abstract
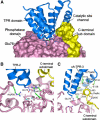
Protein phosphatase 5 (Ppp5) is a serine/threonine protein phosphatase comprising a regulatory tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain N-terminal to its phosphatase domain. Ppp5 functions in signalling pathways that control cellular responses to stress, glucocorticoids and DNA damage. Its phosphatase activity is suppressed by an autoinhibited conformation maintained by the TPR domain and a C-terminal subdomain. By interacting with the TPR domain, heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) and fatty acids including arachidonic acid stimulate phosphatase activity. Here, we describe the structure of the autoinhibited state of Ppp5, revealing mechanisms of TPR-mediated phosphatase inhibition and Hsp90- and arachidonic acid-induced stimulation of phosphatase activity. The TPR domain engages with the catalytic channel of the phosphatase domain, restricting access to the catalytic site. This autoinhibited conformation of Ppp5 is stabilised by the C-terminal alphaJ helix that contacts a region of the Hsp90-binding groove on the TPR domain. Hsp90 activates Ppp5 by disrupting TPR-phosphatase domain interactions, permitting substrate access to the constitutively active phosphatase domain, whereas arachidonic acid prompts an alternate conformation of the TPR domain, destabilising the TPR-phosphatase domain interface.
Figures






References
-
- Andreeva AV, Kutuzov MA (1999) RdgC/PP5-related phosphatases: novel components in signal transduction. Cell Signal 11: 555–562 - PubMed
-
- Barton GJ, Cohen PTW, Barford D (1994) Conservation analysis and structure prediction of the protein serine/threonine phosphatases: sequence similarity with diadenosine tetraphosphatase from E. coli suggests homology to the protein phosphatases. Eur J Biochem 220: 225–237 - PubMed
-
- Borthwick EB, Zeke T, Prescott AR, Cohen PTW (2001) Nuclear localization of protein phosphatase 5 is dependent on the carboxy-terminal region. FEBS Lett 491: 279–284 - PubMed
-
- Brünger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, Read RJ, Rice LM, Simonson T, Warren GL (1998) Crystallography and NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D 54: 905–921 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

