An inflammatory cascade leading to hyperresistinemia in humans
- PMID: 15578112
- PMCID: PMC529430
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0010045
An inflammatory cascade leading to hyperresistinemia in humans
Abstract
Background: Obesity, the most common cause of insulin resistance, is increasingly recognized as a low-grade inflammatory state. Adipocyte-derived resistin is a circulating protein implicated in insulin resistance in rodents, but the role of human resistin is uncertain because it is produced largely by macrophages.
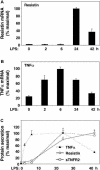
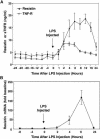
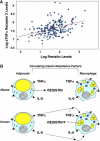
Methods and findings: The effect of endotoxin and cytokines on resistin gene and protein expression was studied in human primary blood monocytes differentiated into macrophages and in healthy human participants. Inflammatory endotoxin induced resistin in primary human macrophages via a cascade involving the secretion of inflammatory cytokines that circulate at increased levels in individuals with obesity. Induction of resistin was attenuated by drugs with dual insulin-sensitizing and anti-inflammatory properties that converge on NF-kappaB. In human study participants, experimental endotoxemia, which produces an insulin-resistant state, causes a dramatic rise in circulating resistin levels. Moreover, in patients with type 2 diabetes, serum resistin levels are correlated with levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor, an inflammatory marker linked to obesity, insulin resistance, and atherosclerosis.
Conclusions: Inflammation is a hyperresistinemic state in humans, and cytokine induction of resistin may contribute to insulin resistance in endotoxemia, obesity, and other inflammatory states.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. Epidemiologic trends in overweight and obesity. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2003;32:741–760. - PubMed
-
- Flier JS. Obesity wars: Molecular progress confronts an expanding epidemic. Cell. 2004;116:337–350. - PubMed
-
- Sowers JR, Frohlich ED. Insulin and insulin resistance: Impact on blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Med Clin North Am. 2004;88:63–82. - PubMed
-
- Haffner SM. Insulin resistance, inflammation, and the prediabetic state. Am J Cardiol. 2003;92:18J-26J. - PubMed
-
- Rajala MW, Scherer PE. Minireview: The adipocyte—at the crossroads of energy homeostasis, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Endocrinology. 2003;144:3765–3773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 RR15532/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000040/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK49210/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 RR015532/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK049780/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK049210/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00040/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL73278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK49780/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK019525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK19525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

