Ablation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-gamma reduces the severity of acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 15579443
- PMCID: PMC1618701
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63251-8
Ablation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-gamma reduces the severity of acute pancreatitis
Abstract
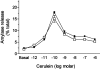
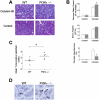
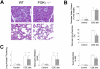
In pancreatic acini, the G-protein-activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase-gamma (PI3K gamma) regulates several key pathological responses to cholecystokinin hyperstimulation in vitro. Thus, using mice lacking PI3K gamma, we studied the function of this enzyme in vivo in two different models of acute pancreatitis. The disease was induced by supramaximal concentrations of cerulein and by feeding mice a choline-deficient/ethionine-supplemented diet. Although the secretive function of isolated pancreatic acini was identical in mutant and control samples, in both models, genetic ablation of PI3K gamma significantly reduced the extent of acinar cell injury/necrosis. In agreement with a protective role of apoptosis in pancreatitis, PI3K gamma-deficient pancreata showed an increased number of apoptotic acinar cells, as determined by terminal dUTP nick-end labeling and caspase-3 activity. In addition, neutrophil infiltration within the pancreatic tissue was also reduced, suggesting a dual action of PI3K gamma, both in the triggering events within acinar cells and in the subsequent neutrophil recruitment and activation. Finally, the lethality of the choline-deficient/ethionine-supplemented diet-induced pancreatitis was significantly reduced in mice lacking PI3K gamma. Our results thus suggest that inhibition of PI3K gamma may be of therapeutic value in acute pancreatitis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 7;20(41):15190-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15190. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25386068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of nuclear factor kappa B and severe hepatic necrosis may mediate systemic inflammation in choline-deficient/ethionine-supplemented diet-induced pancreatitis.Pancreas. 2006 Oct;33(3):260-7. doi: 10.1097/01.mpa.0000240599.95817.34. Pancreas. 2006. PMID: 17003648
-
The role of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and neutrophils in acute pancreatitis and pancreatitis-associated lung injury.Gastroenterology. 1999 Mar;116(3):694-701. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70192-7. Gastroenterology. 1999. PMID: 10029629
-
Relationship between severity, necrosis, and apoptosis in five models of experimental acute pancreatitis.Am J Physiol. 1995 Nov;269(5 Pt 1):C1295-304. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.269.5.C1295. Am J Physiol. 1995. PMID: 7491921
-
Acute experimental hemorrhagic-necrotizing pancreatitis induced by feeding a choline-deficient, ethionine-supplemented diet. Methodology and standards.Eur Surg Res. 1992;24 Suppl 1:40-54. doi: 10.1159/000129238. Eur Surg Res. 1992. PMID: 1601023 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 7;20(41):15190-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15190. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25386068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p110γ deficiency protects against pancreatic carcinogenesis yet predisposes to diet-induced hepatotoxicity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jul 16;116(29):14724-14733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1813012116. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31266893 Free PMC article.
-
Acanthopanax versus 3-Methyladenine Ameliorates Sodium Taurocholate-Induced Severe Acute Pancreatitis by Inhibiting the Autophagic Pathway in Rats.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:8369704. doi: 10.1155/2016/8369704. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 28115794 Free PMC article.
-
The role of PI3Kγ in the immune system: new insights and translational implications.Nat Rev Immunol. 2022 Nov;22(11):687-700. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00701-8. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35322259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits zymogen activation by suppressing vacuolar ATPase activation in cerulein-stimulated pancreatic acinar cells.Genes Nutr. 2020 Mar 23;15(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12263-020-00664-2. Genes Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32293245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steer ML. Etiology and pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Go VLV, Dimango EP, Gardner JD, Lebenthal E, Reber HA, Scheele GA, editors. New York: Raven; The PancreasBiology, Pathobiology, and Disease. 1993:pp 581–592.
-
- Steer M. Pancreatitis severity: who calls the shots? Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1168–1172. - PubMed
-
- Steer ML. Early events in acute pancreatitis. Bailliere’s Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 1999;13:213–225. - PubMed
-
- Hofbauer B, Saluja AK, Lerch MM, Bhagat L, Bhatia M, Lee HS, Frossard JL, Adler G, Steer ML. Intra-acinar cell activation of trypsinogen during caerulein-induced pancreatitis in rats. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:G352–G362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

