Locus 'decontraction' and centromeric recruitment contribute to allelic exclusion of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene
- PMID: 15580273
- PMCID: PMC1592471
- DOI: 10.1038/ni1150
Locus 'decontraction' and centromeric recruitment contribute to allelic exclusion of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene
Abstract
Allelic exclusion of immunoglobulin genes ensures the expression of a single antibody molecule in B cells through mostly unknown mechanisms. Large-scale contraction of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain (Igh) locus facilitates rearrangements between Igh variable (V(H)) and diversity gene segments in pro-B cells. Here we show that these long-range interactions are mediated by 'looping' of individual Igh subdomains. The Igk locus also underwent contraction by looping in small pre-B and immature B cells, demonstrating that immunoglobulin loci are in a contracted state in rearranging cells. Successful Igh recombination induced the rapid reversal of locus contraction in response to pre-B cell receptor signaling, which physically separated the distal V(H) genes from the proximal Igh domain, thus preventing further rearrangements. In the absence of locus contraction, only the four most proximal V(H) genes escaped allelic exclusion in immature mu-transgenic B lymphocytes. Pre-B cell receptor signaling also led to rapid repositioning of one Igh allele to repressive centromeric domains in response to downregulation of interleukin 7 signaling. These data link both locus 'decontraction' and centromeric recruitment to the establishment of allelic exclusion at the Igh locus.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures


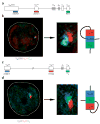

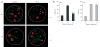



Comment in
-
A move to exclude.Nat Immunol. 2005 Feb;6(2):128-30. doi: 10.1038/ni0205-128. Nat Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15662439 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hesslein DG, Schatz DG. Factors and forces controlling V(D)J recombination. Adv Immunol. 2001;78:169–232. - PubMed
-
- Bassing CH, Swat W, Alt FW. The mechanism and regulation of chromosomal V(D)J recombination. Cell. 2002;109:S45–S55. - PubMed
-
- Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW, Rajewsky K. The lingering enigma of the allelic exclusion mechanism. Cell. 2004;118:539–544. - PubMed
-
- Yancopoulos GD, Alt FW. Developmentally controlled and tissue-specific expression of unrearranged VH gene segments. Cell. 1985;40:271–281. - PubMed
-
- Stanhope-Baker P, Hudson KM, Shaffer AL, Constantinescu A, Schlissel MS. Cell type-specific chromatin structure determines the targeting of V(D)J recombinase activity in vitro. Cell. 1996;85:887–897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

